Soutenu Analysis
Posted by Paul Zaichik on

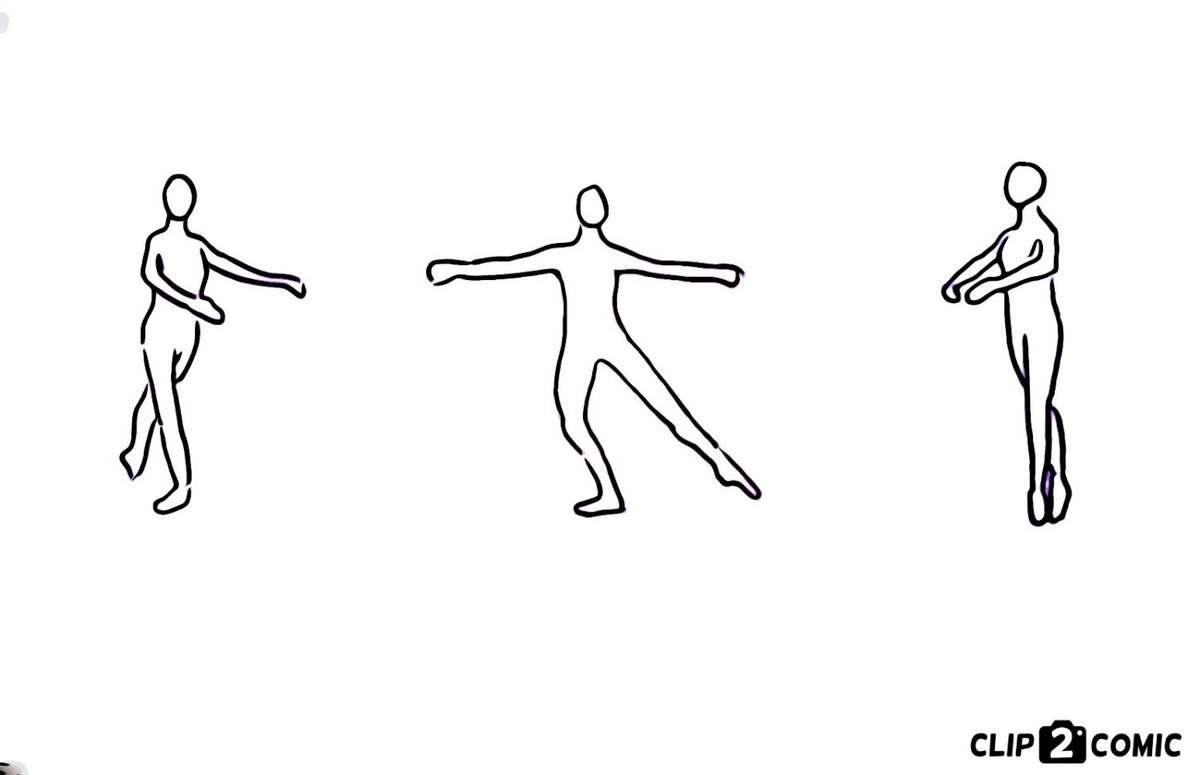
Soutenu is a term in classical ballet which means “sustained.” The ballet dancer turns in sus-sous or in fifth position en pointé and ends up with the opposite foot in front.
Let's take a look at the video below:
We will be discussing the seven stances included in a Soutenu. We will be looking at the positions of your spine, hip, knees, ankles, shoulders, and your elbows at each given stance; and the prime muscles involved at each body segments when you are performing the actions.

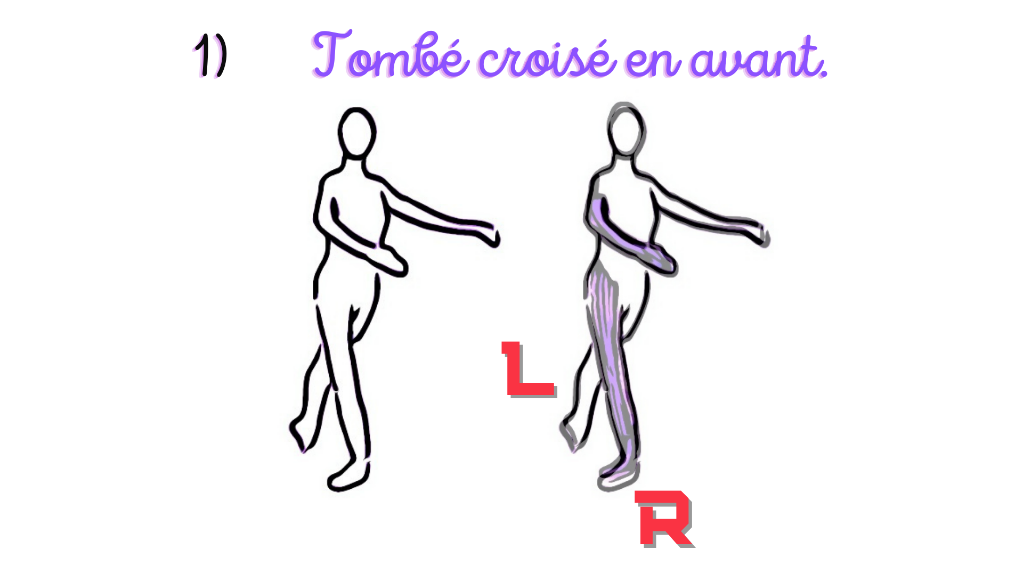
The first stance includes: Tombé croisé en avant.
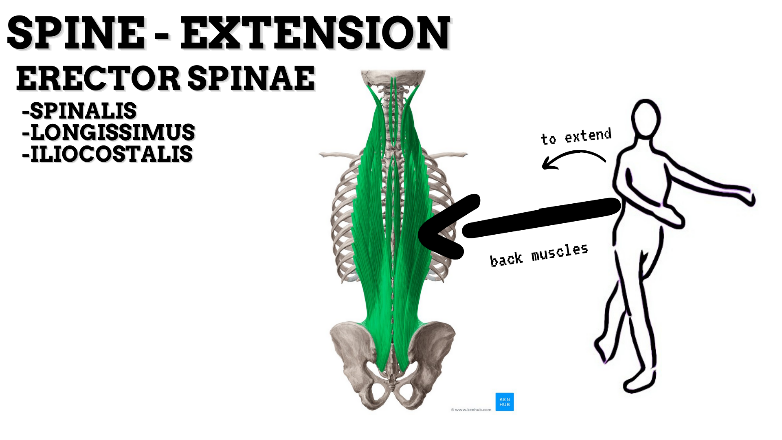
MAJOR JOINT: SPINE
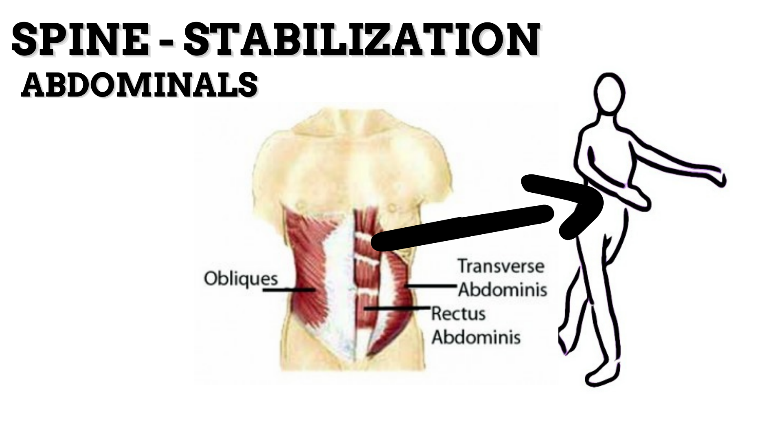
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
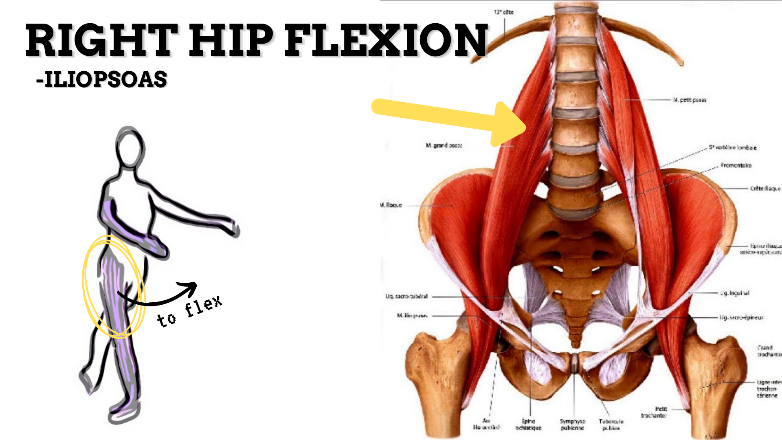
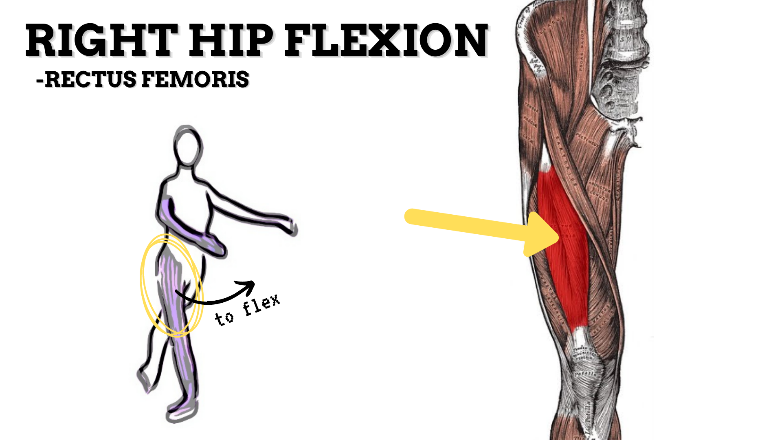
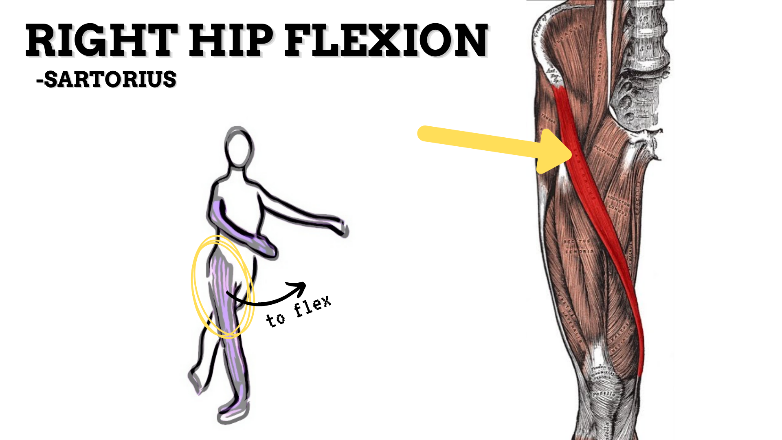
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: R FLEXION, concentric
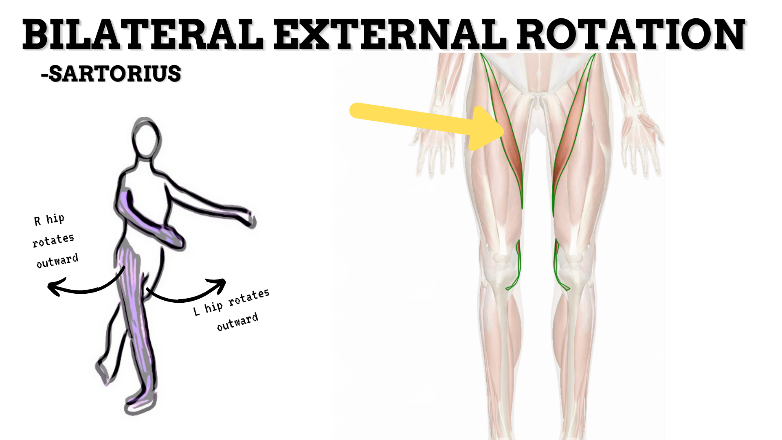
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
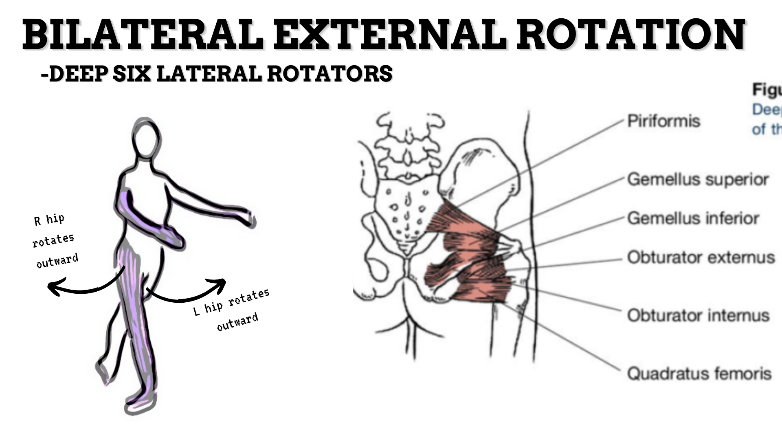
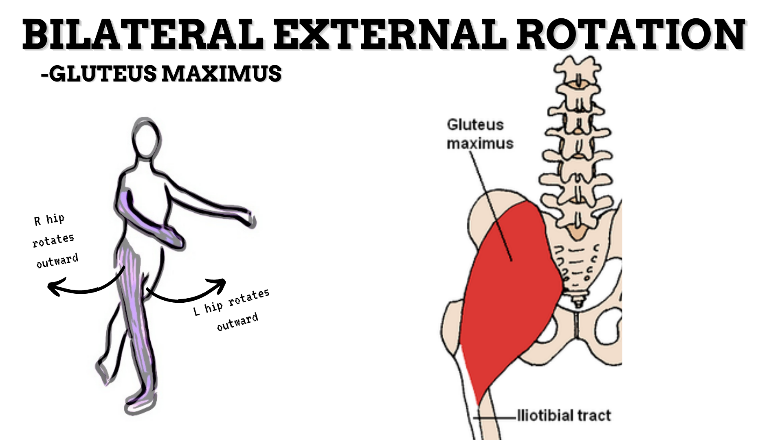
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ER, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
To achieve and maintain external rotation of the hip: Strengthen the deep lateral rotators or stretch the hip internal rotators, capsules, and anterior ligaments.
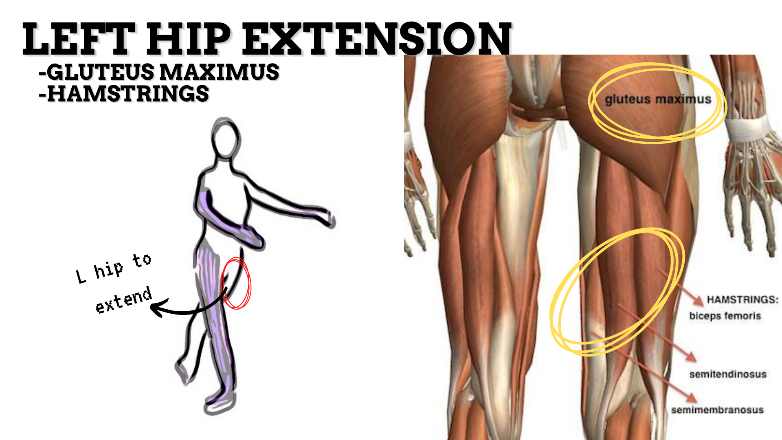
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: L EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
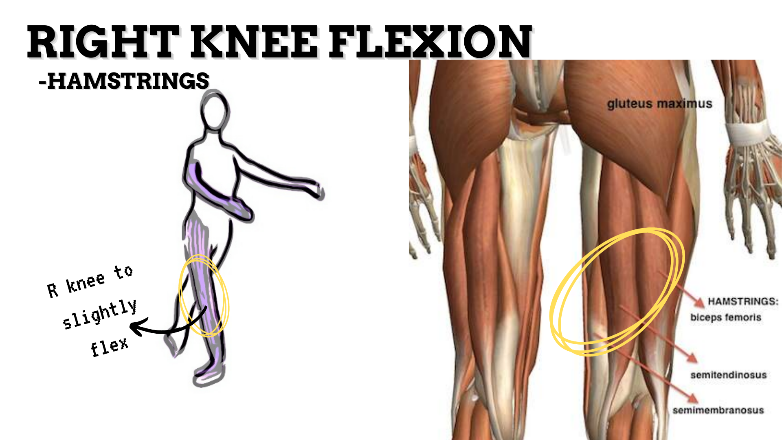
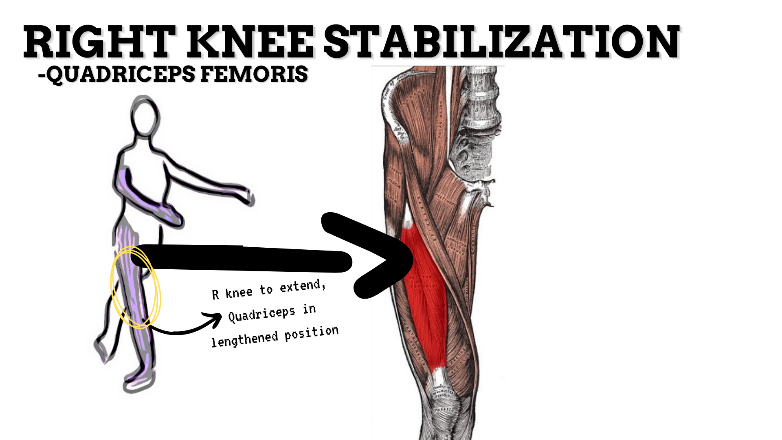
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: R FLEXION, concentric stabilized by QUADRICEPS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS
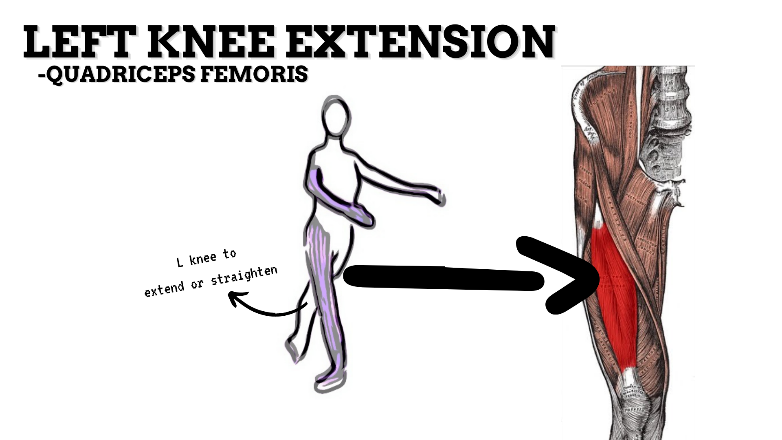
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: L EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
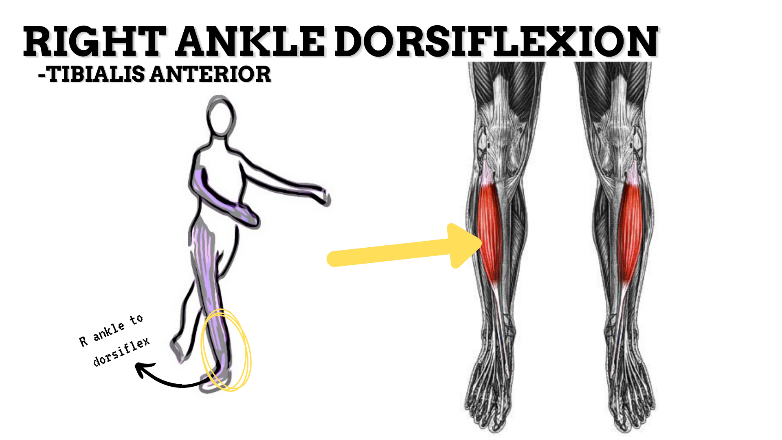
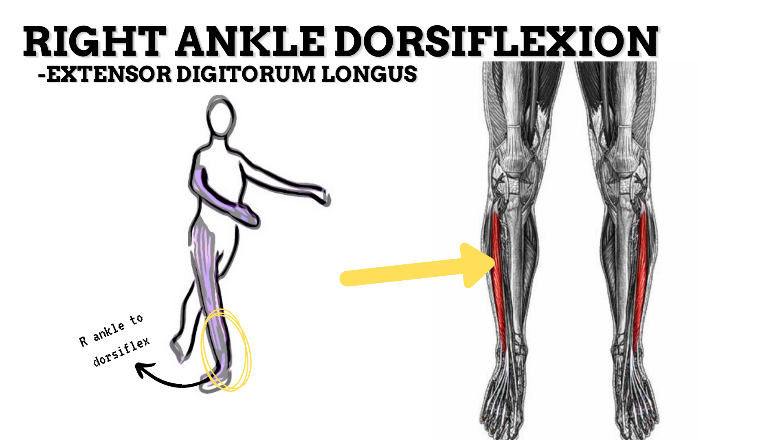
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: R DF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: TIBIALIS ANTERIOR, EDL
PRIME MOVER: TIBIALIS ANTERIOR, EDL
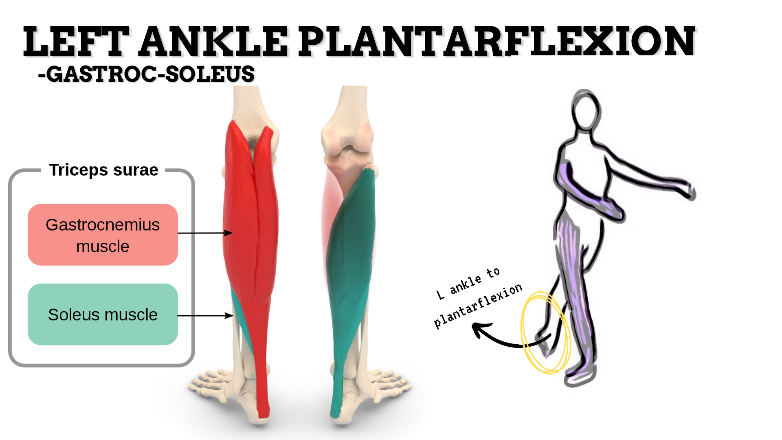
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: L PF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
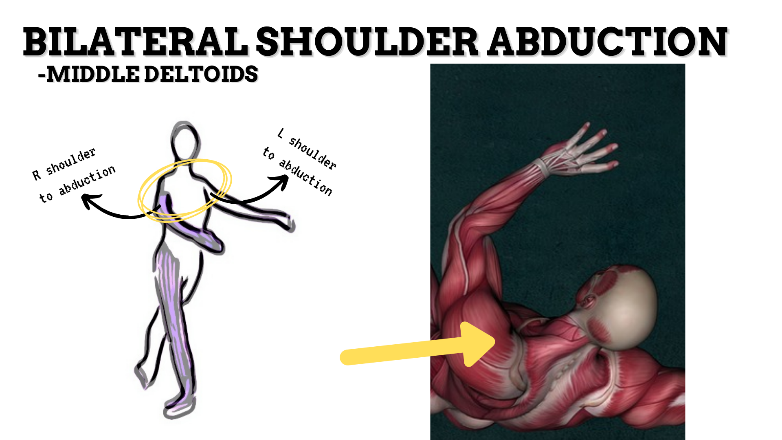
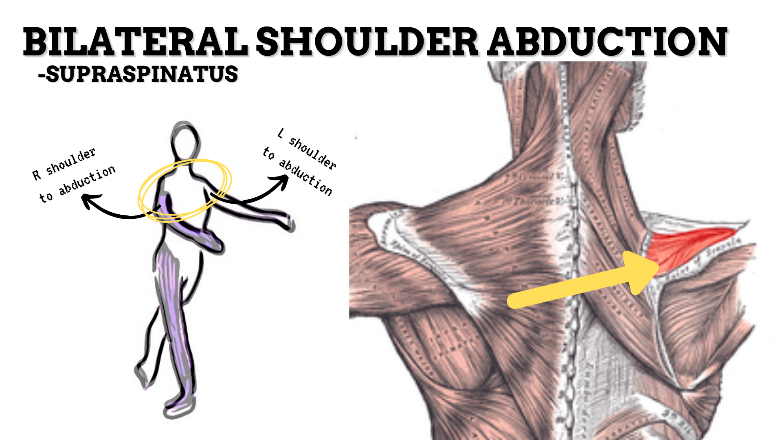
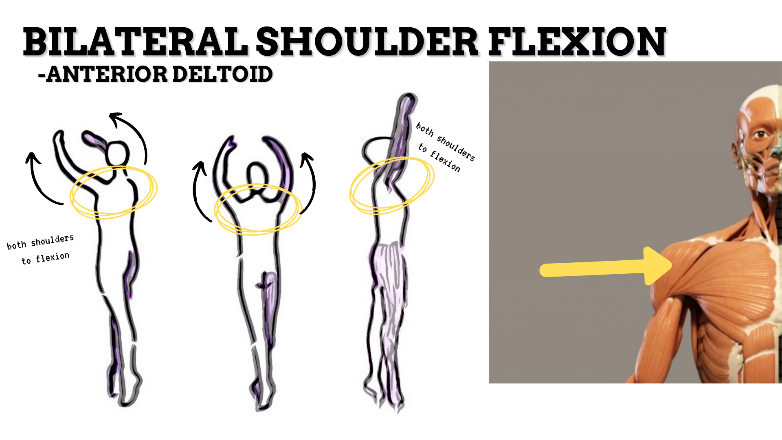
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ABDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
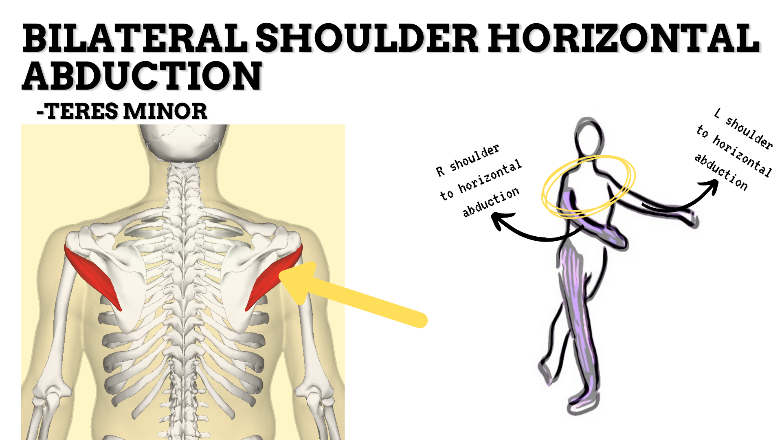
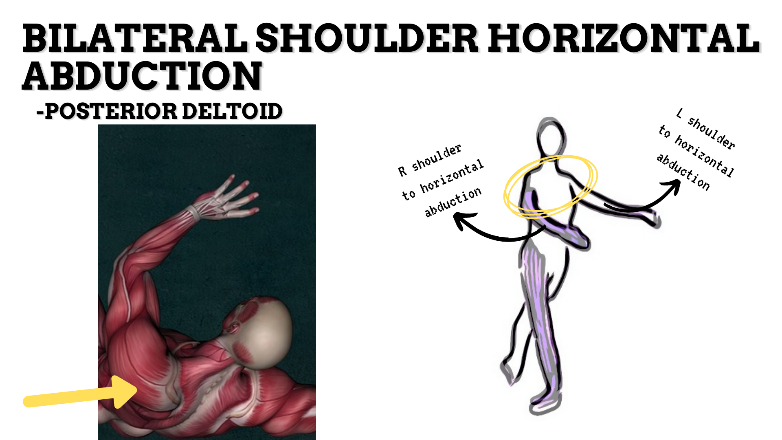
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL HORIZONTAL ABDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: TERES MINOR, POSTERIOR DELTOID
PRIME MOVER: TERES MINOR, POSTERIOR DELTOID
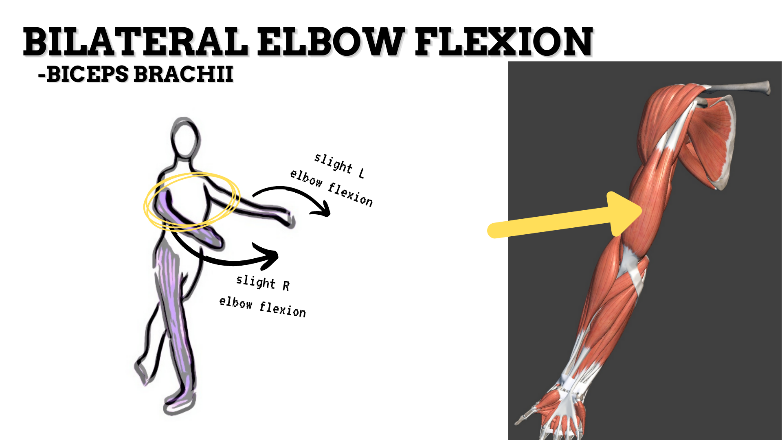
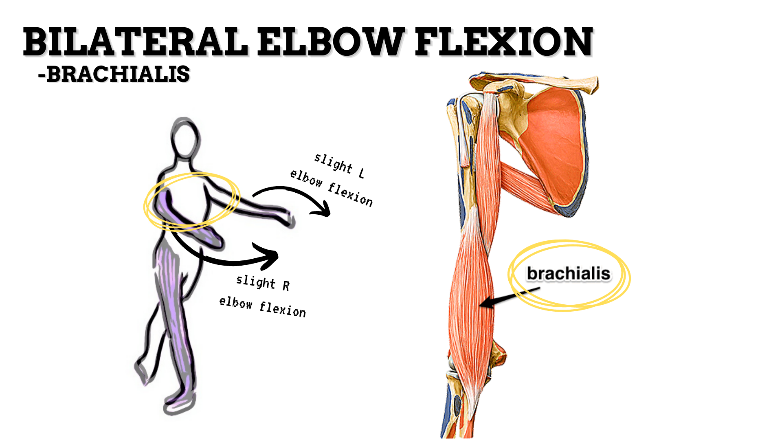
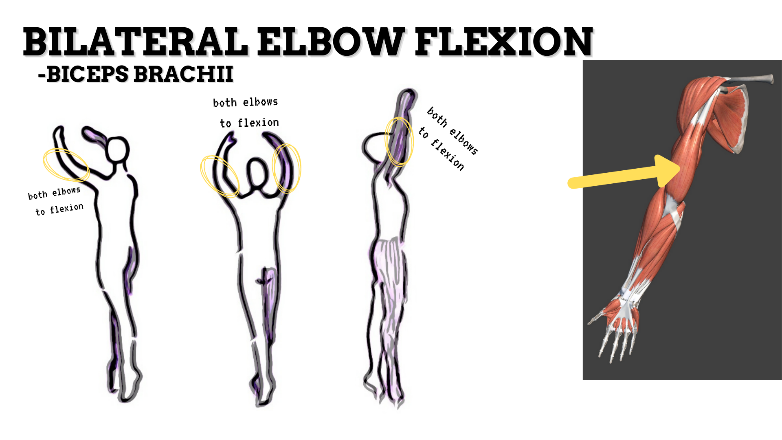
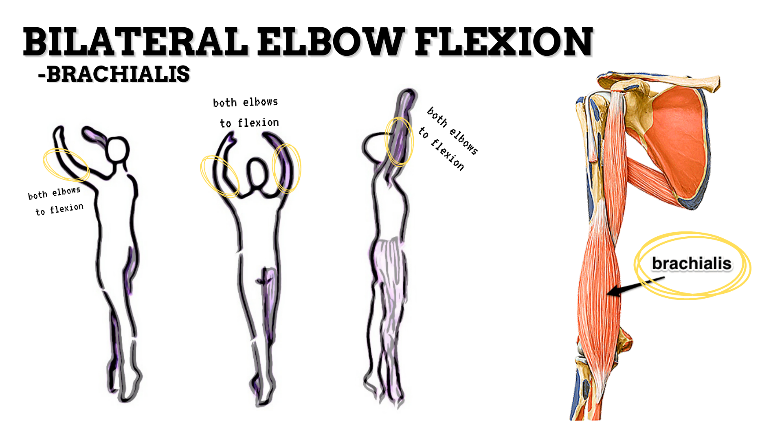
MAJOR JOINT: ELBOW
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
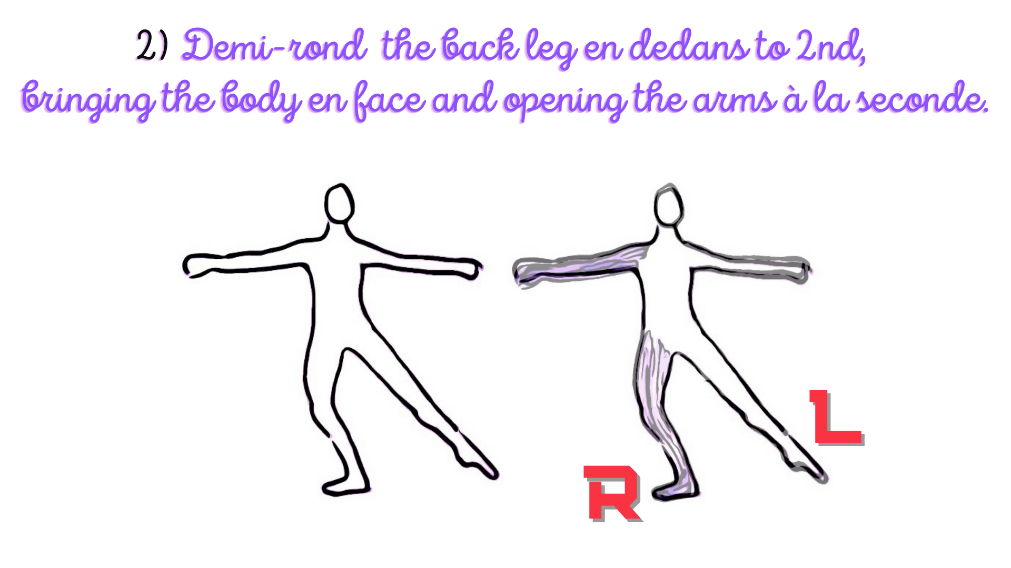
The second stance includes: to demi-rond the back leg
en dedans to 2nd, bringing the body en face and opening the arms à la seconde.
en dedans to 2nd, bringing the body en face and opening the arms à la seconde.
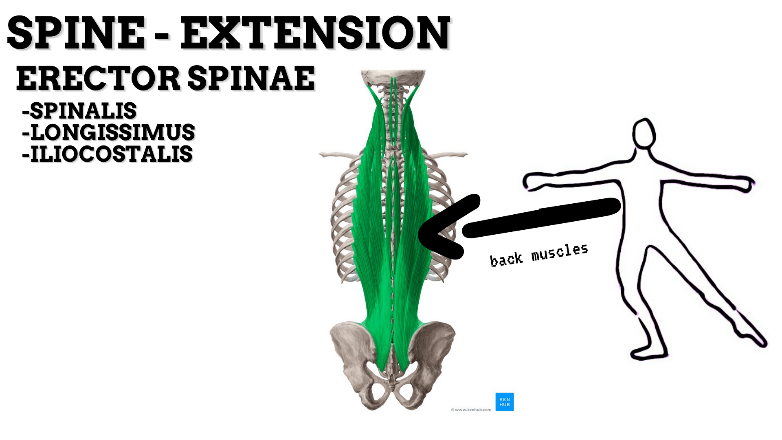
MAJOR JOINT: SPINE
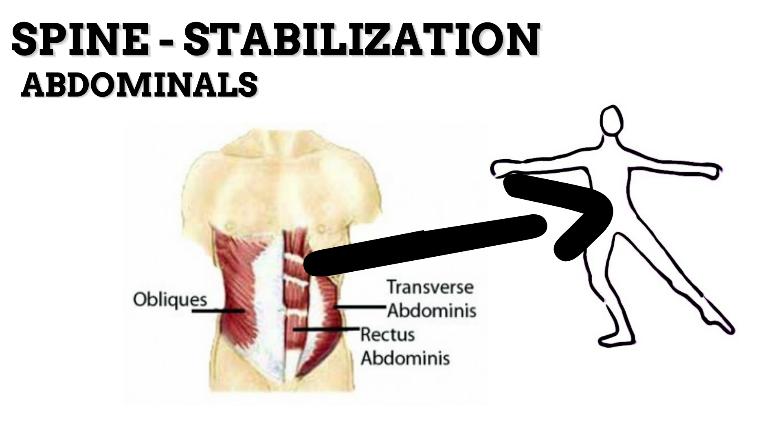
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
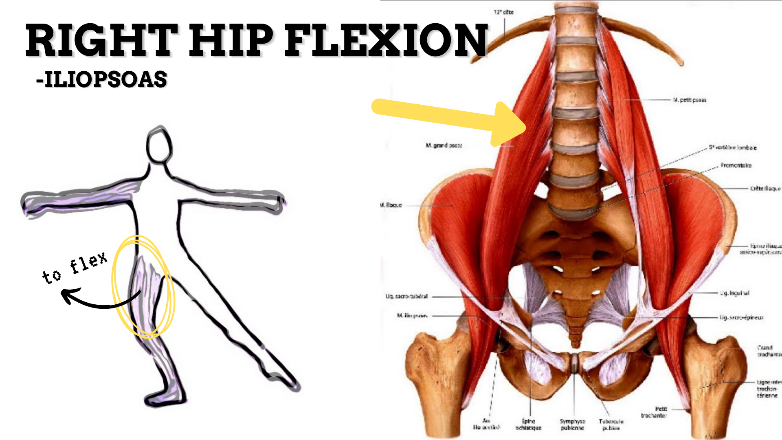
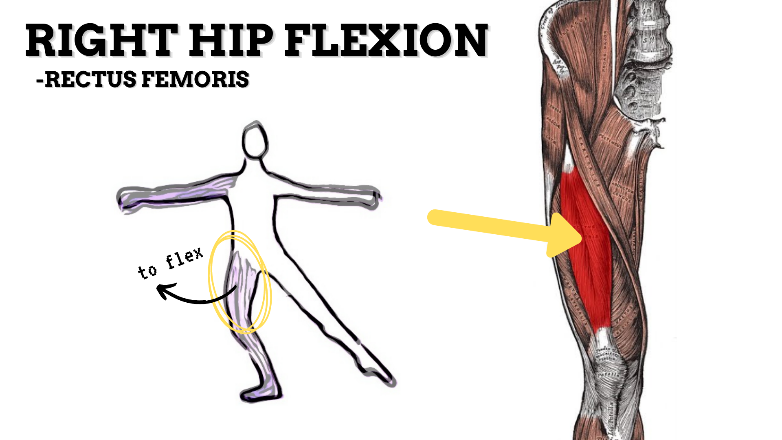
MOVEMENT: R FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
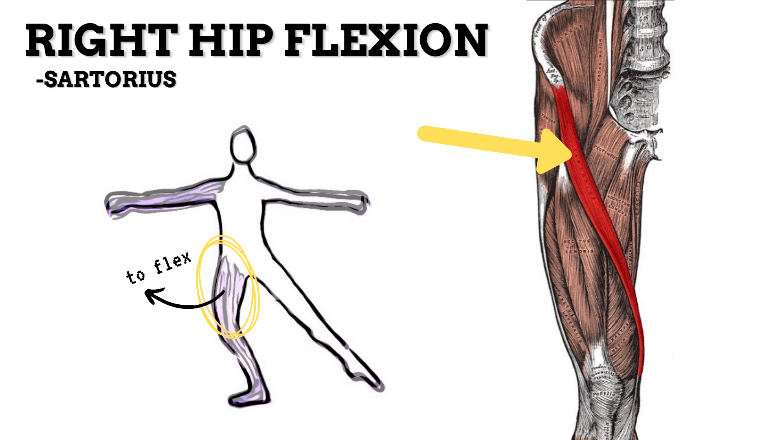
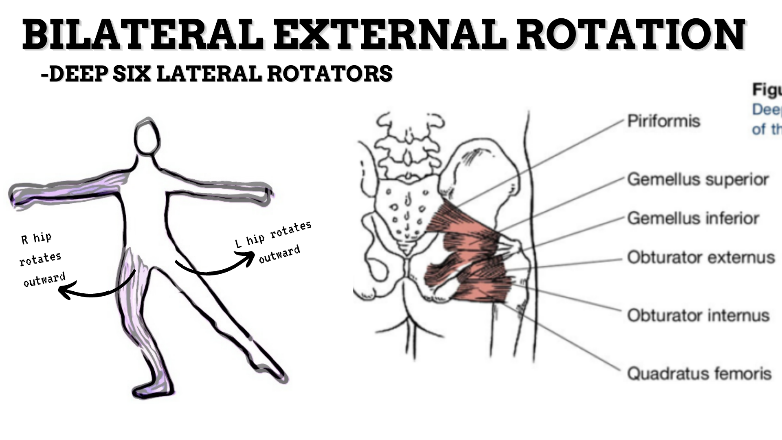
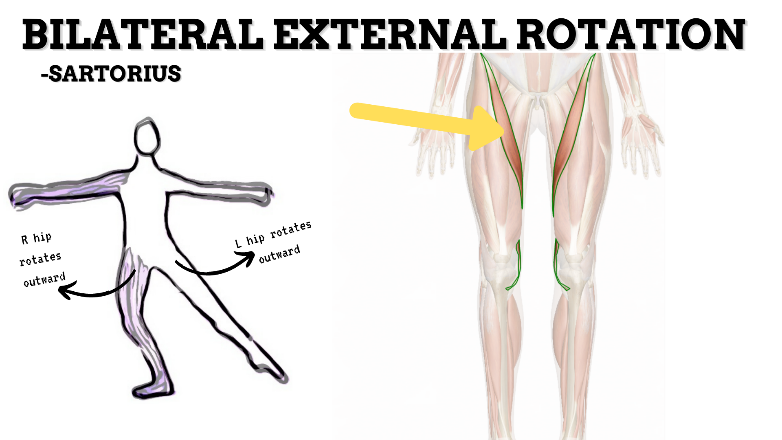
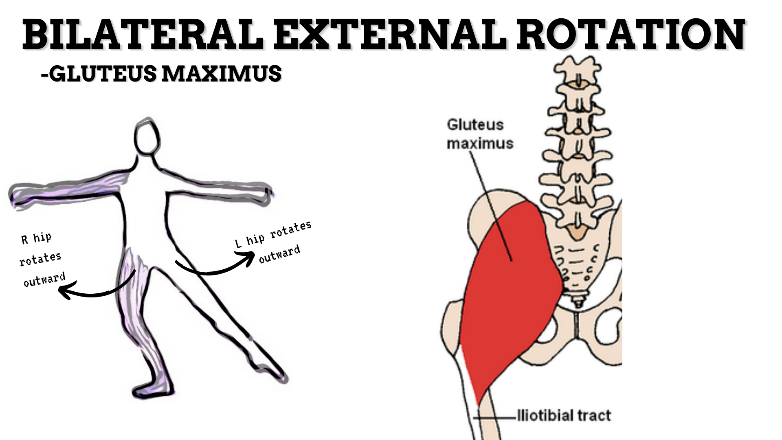
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ER, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
To achieve and maintain external rotation of the hip: Strengthen the deep lateral rotators or stretch the hip internal rotators, capsules, and anterior ligaments.
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: L ABDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MEDIUS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MEDIUS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
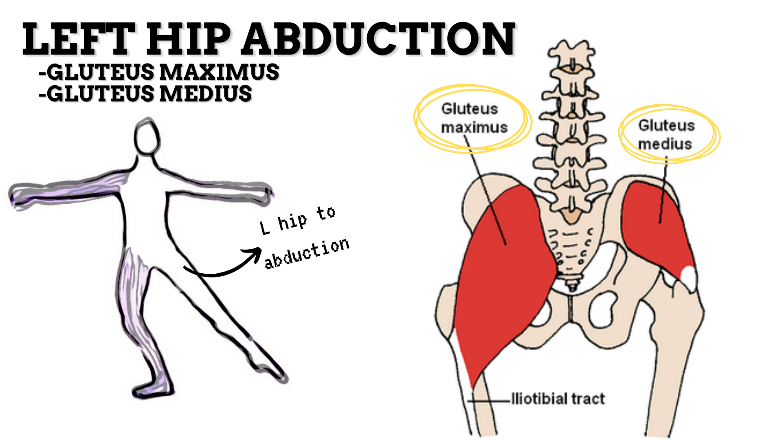
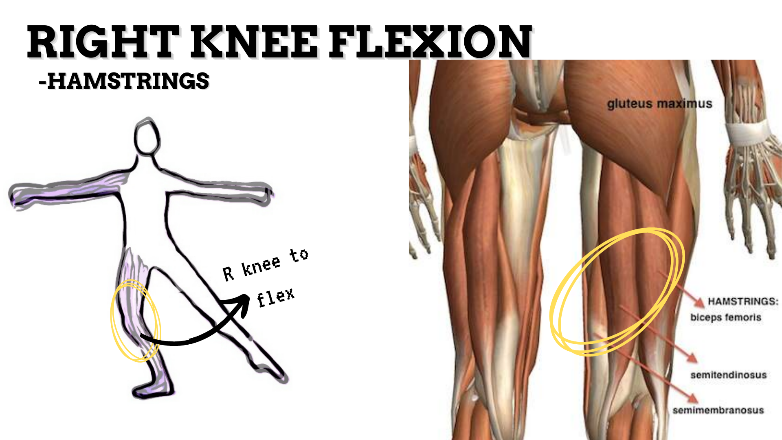
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: R FLEXION, concentric stabilized by QUADRICEPS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS
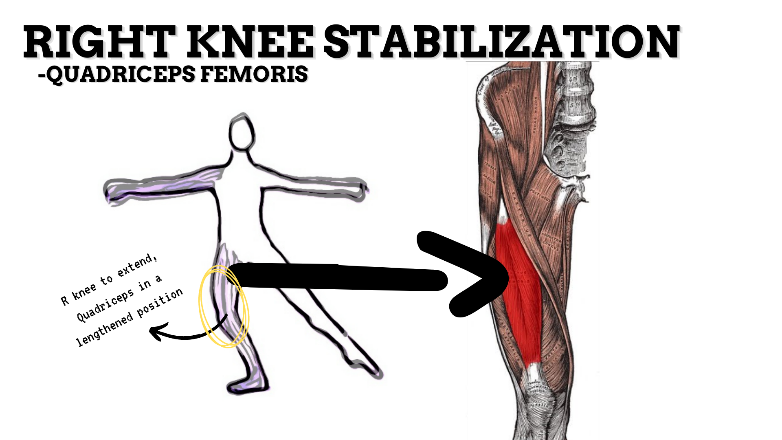
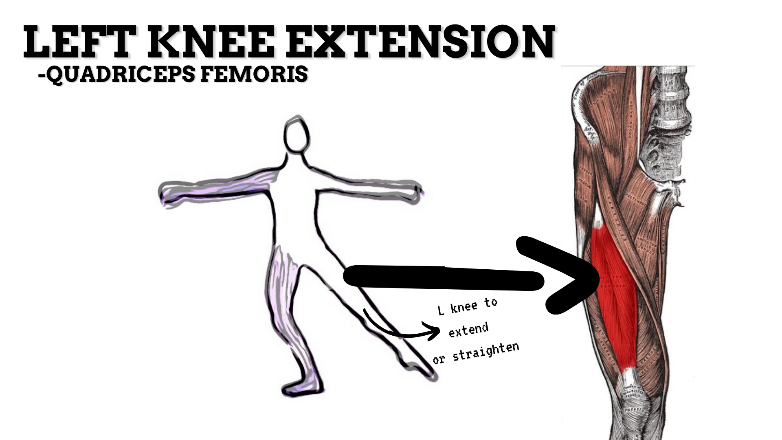
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: L EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: R DF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: TIBIALIS ANTERIOR, EDL
PRIME MOVER: TIBIALIS ANTERIOR, EDL
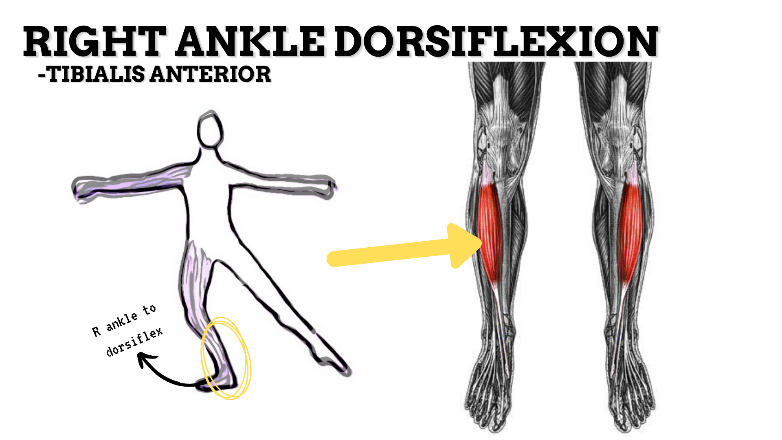
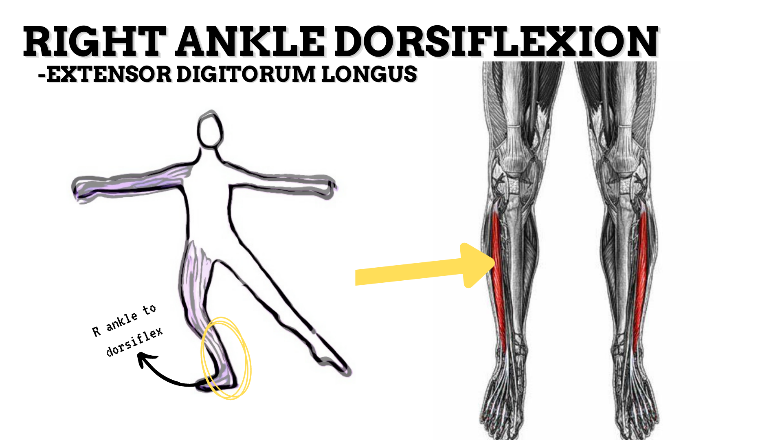
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
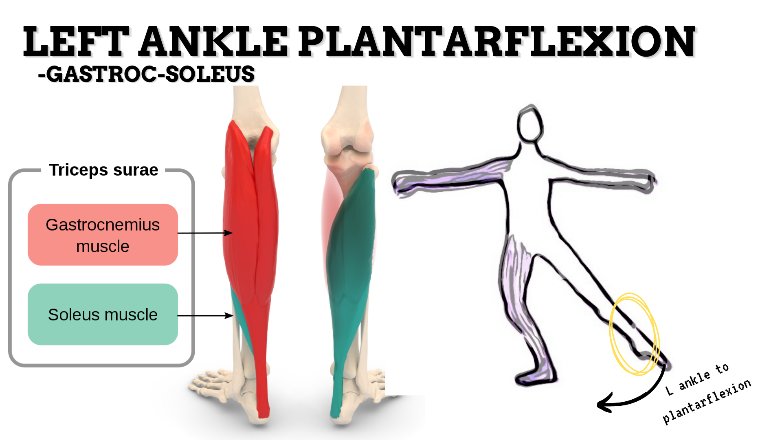
MOVEMENT: L PF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
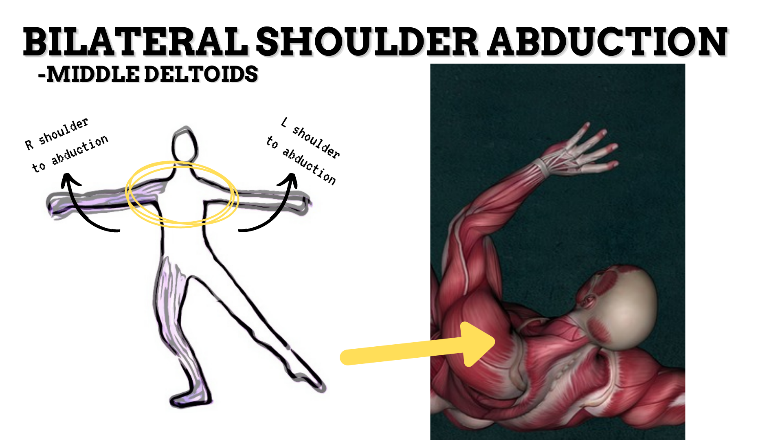
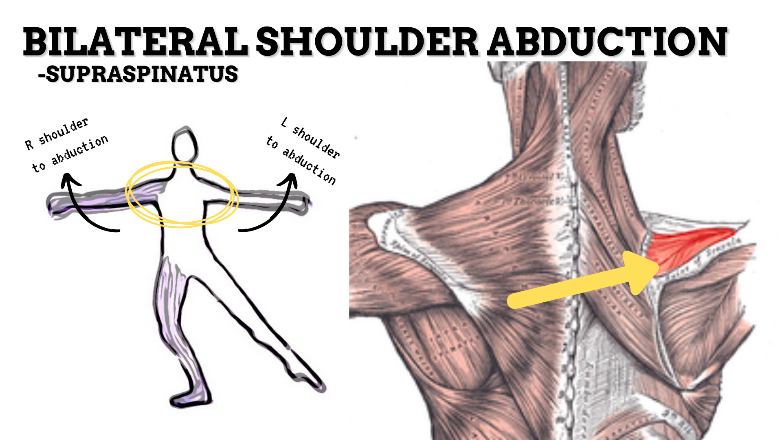
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ABDUCTION to nearly 90 degrees, concentric
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
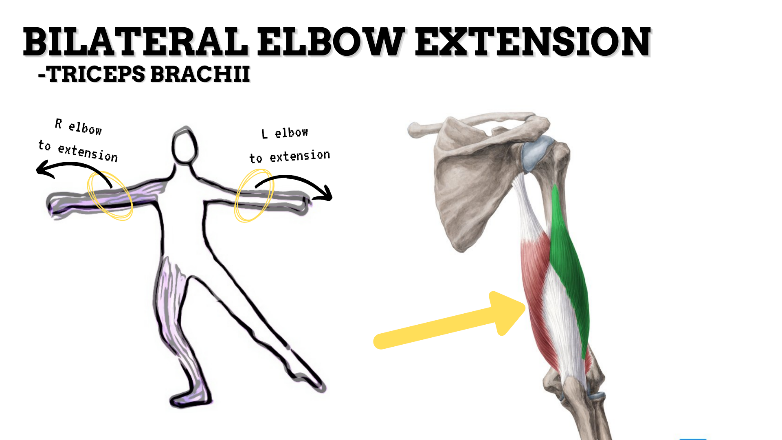
MAJOR JOINT: ELBOW
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: TRICEPS BRACHII
PRIME MOVER: TRICEPS BRACHII
Start working on your Ballet Techniques today! Click on the picture below to learn about our Ballet & Dance Combo:
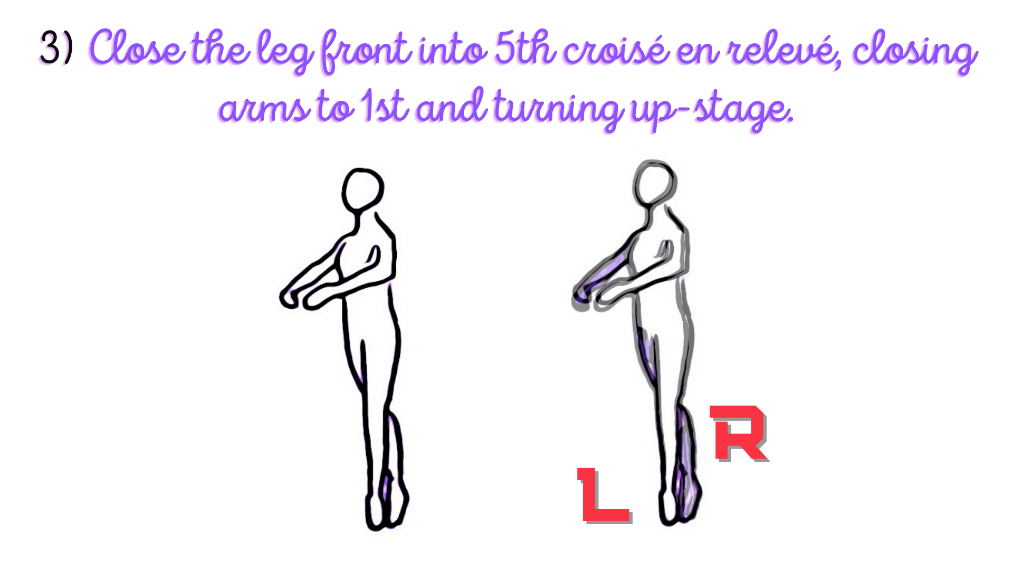
The third stance includes: to close the leg front into 5th croisé en relevé, closing arms to 1st and turning up-stage.
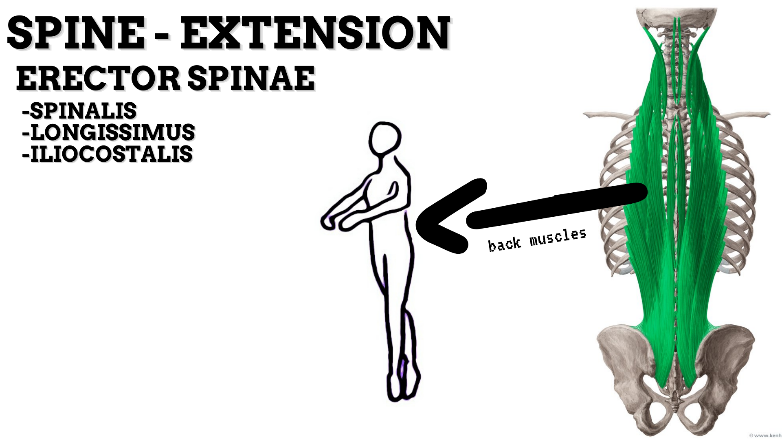
MAJOR JOINT: SPINE
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
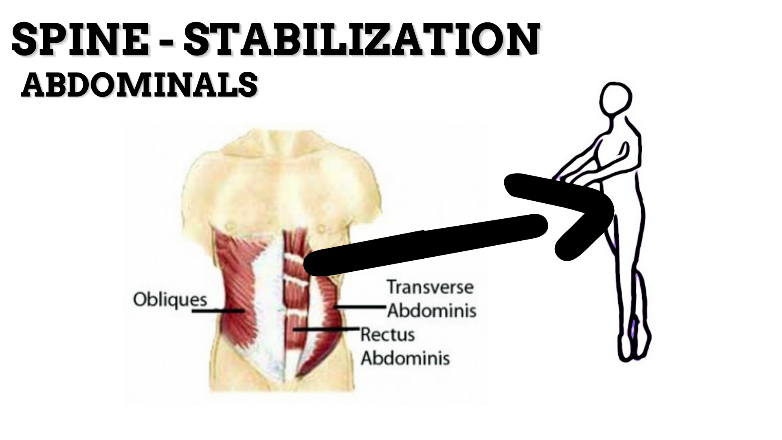
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
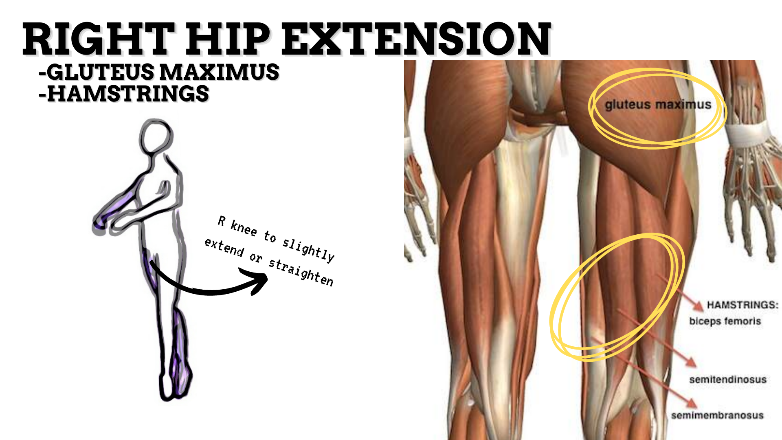
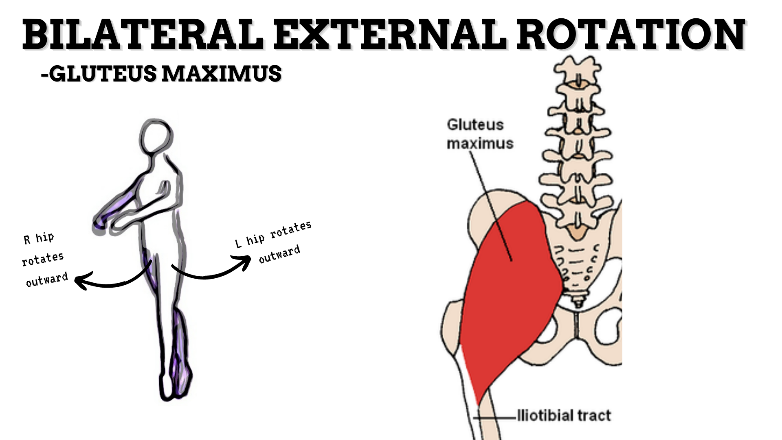
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ER, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
To achieve and maintain external rotation of the hip: Strengthen the deep lateral rotators or stretch the hip internal rotators, capsules, and anterior ligaments.
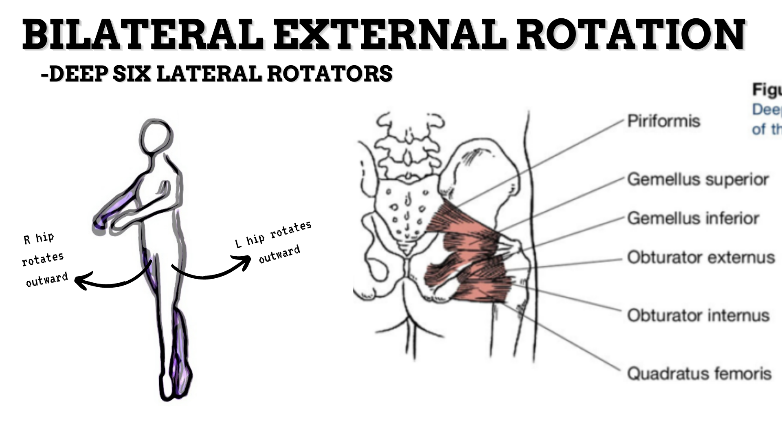
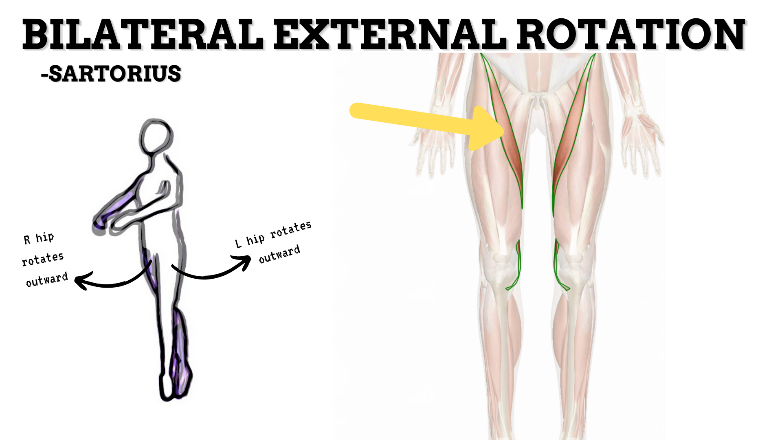
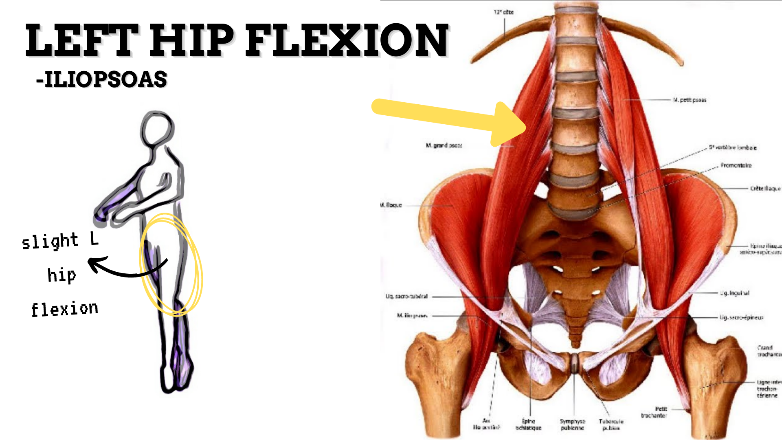
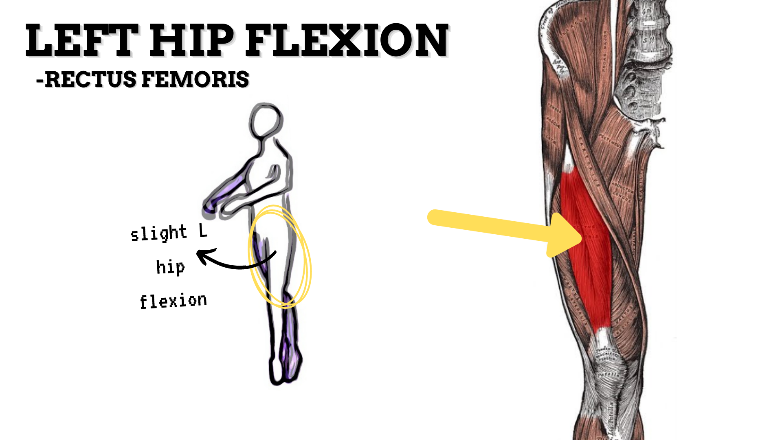
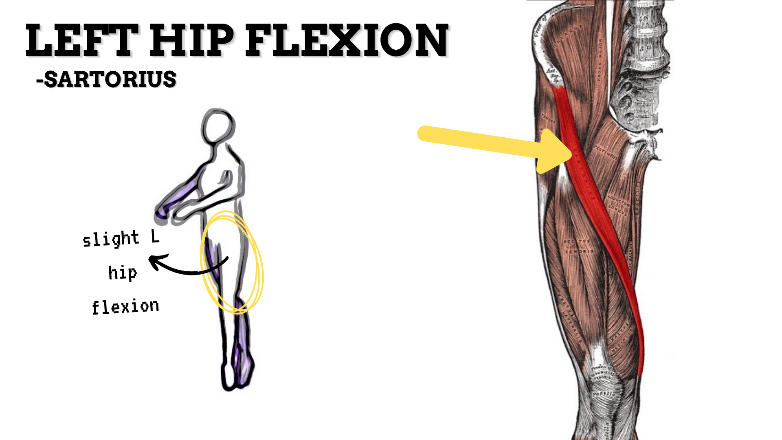
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: L SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
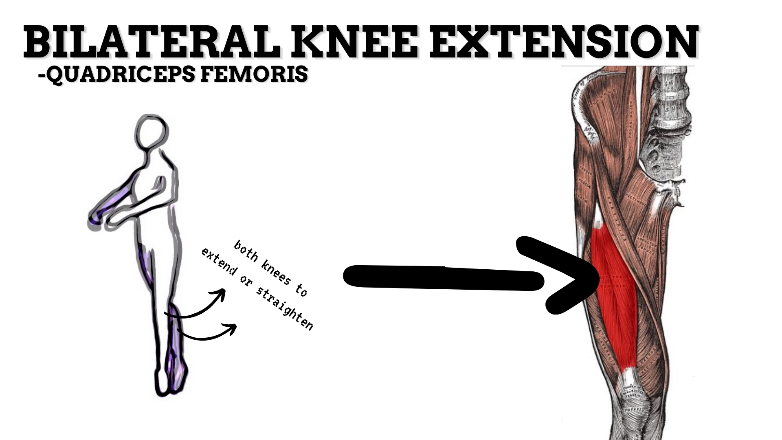
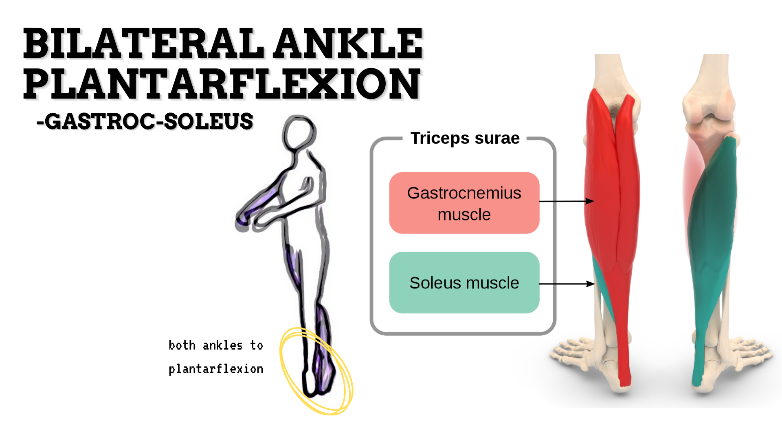
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL PF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
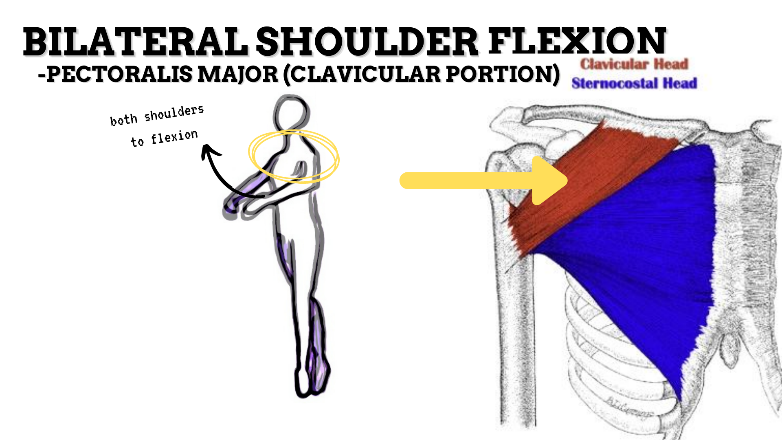
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
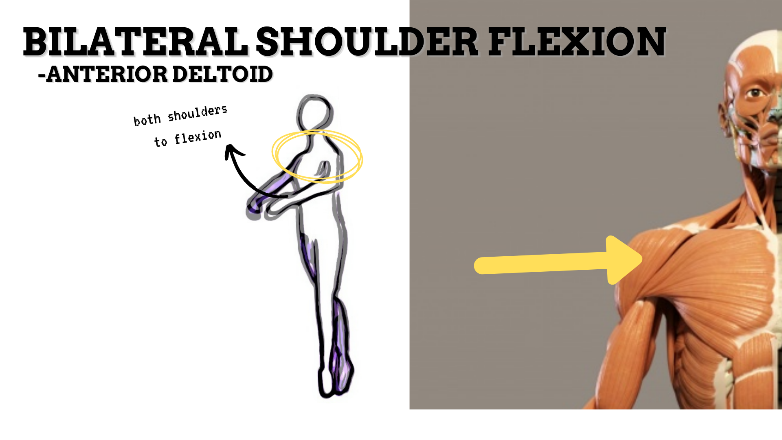
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
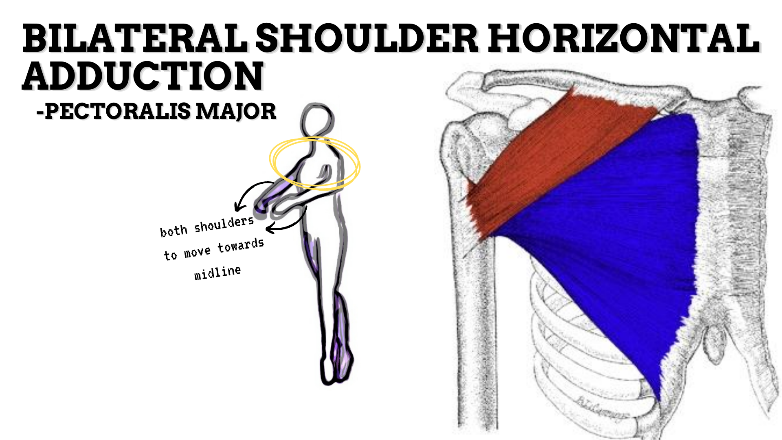
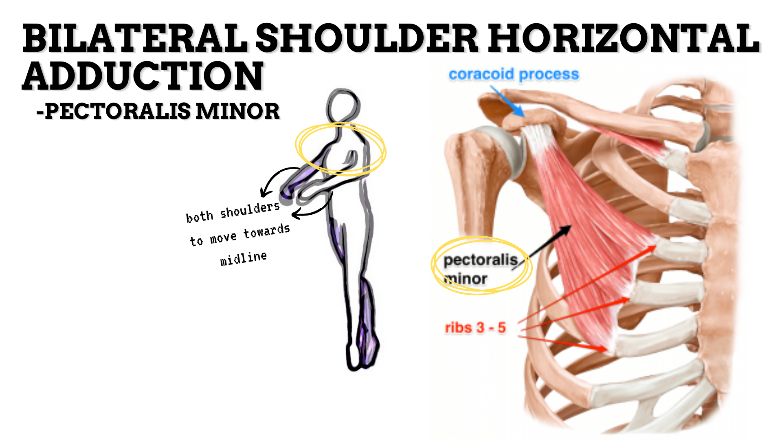
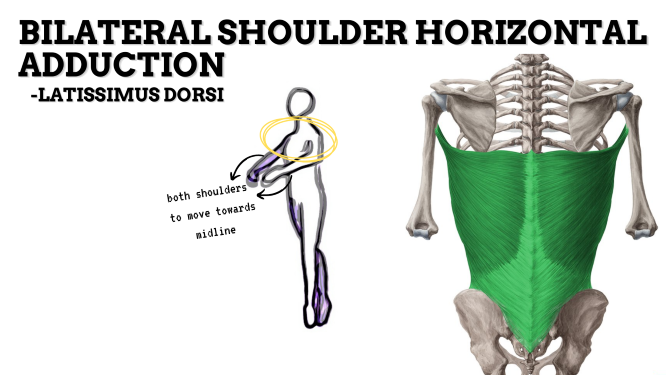
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL HORIZONTAL ADDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MINOR, PECTORALIS MAJOR, LATISSIMUS DORSI
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MINOR, PECTORALIS MAJOR, LATISSIMUS DORSI
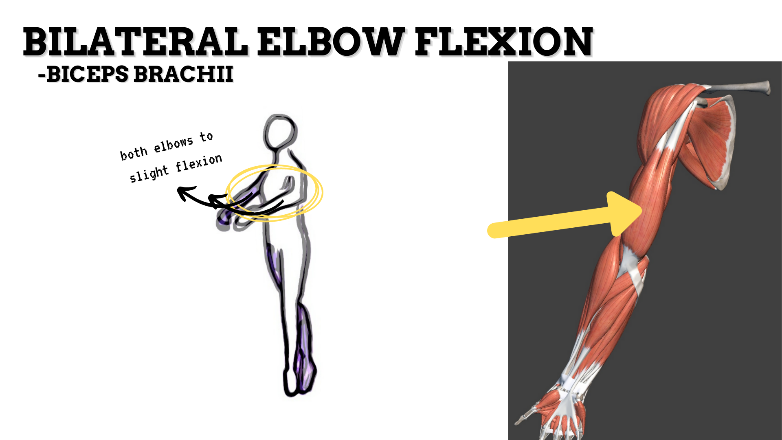
MAJOR JOINT: ELBOW
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
The fourth to sixth stance includes: to transfer the weight onto the front foot, continuing to turn upstage, readjusting the back foot around the 5th in front, and lifting the arms to 5th en haut.
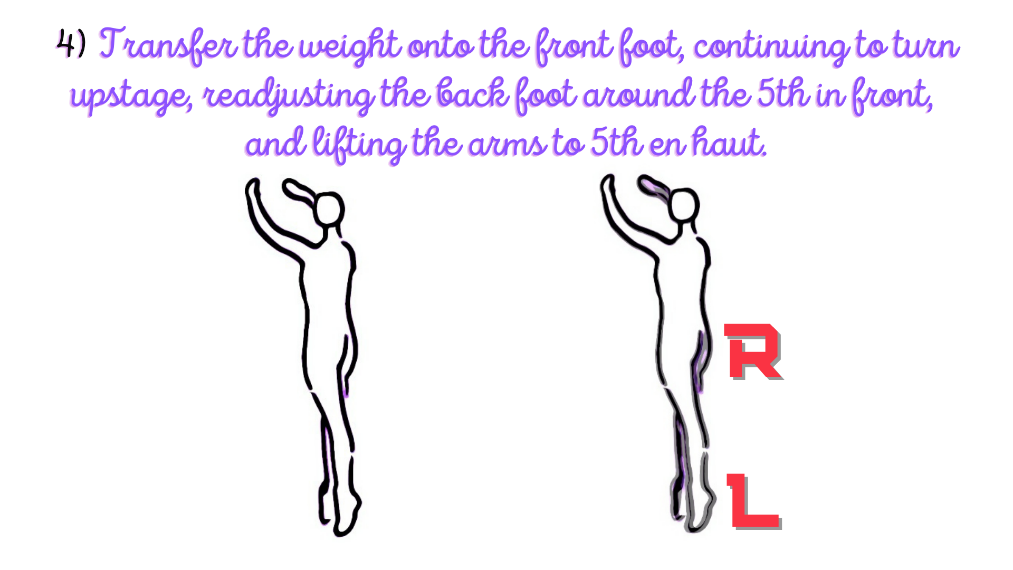
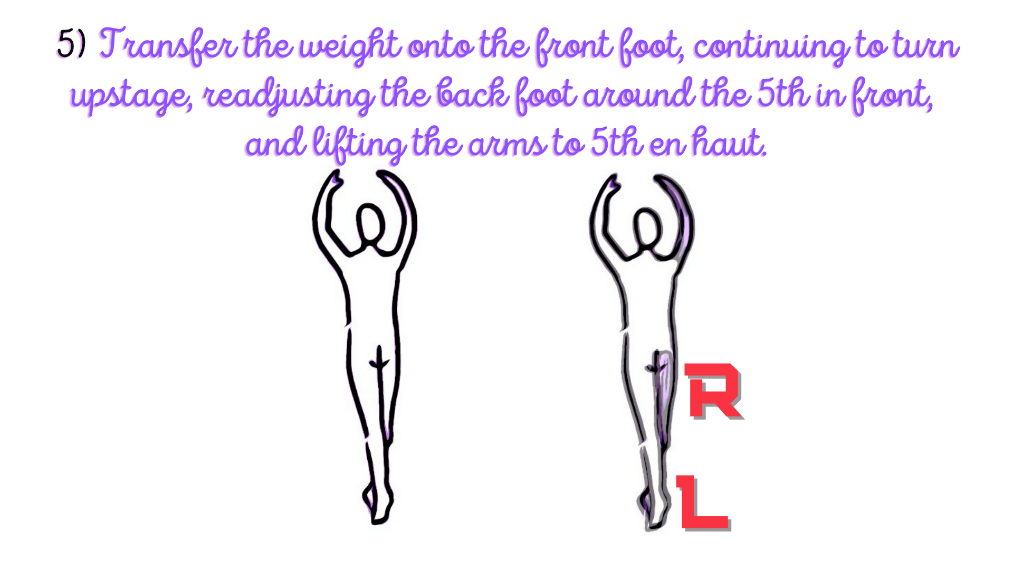
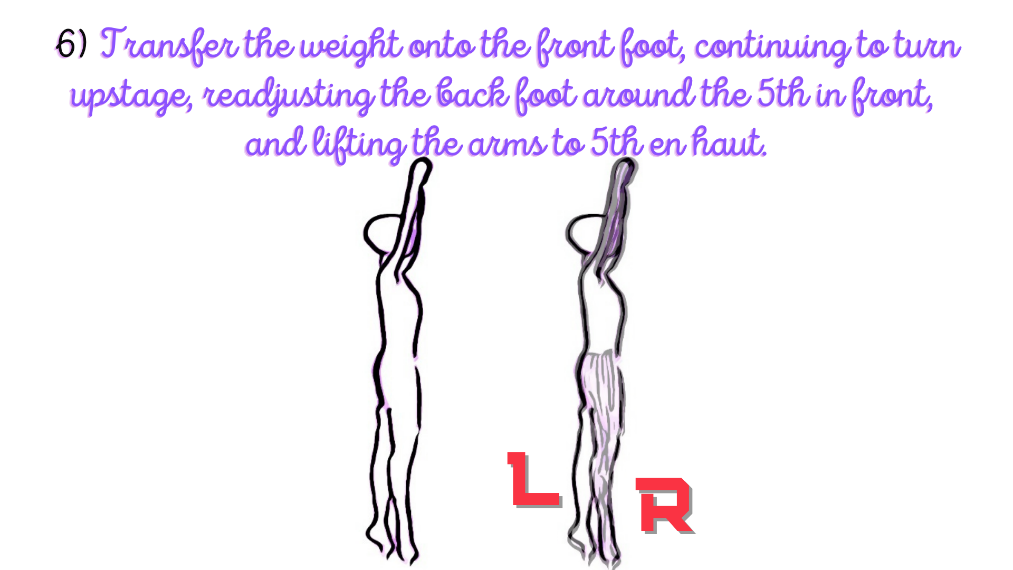
MAJOR JOINT: SPINE
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: ERECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
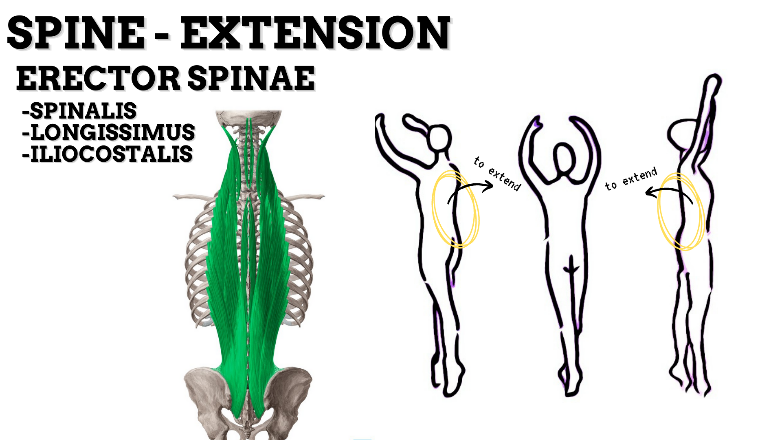
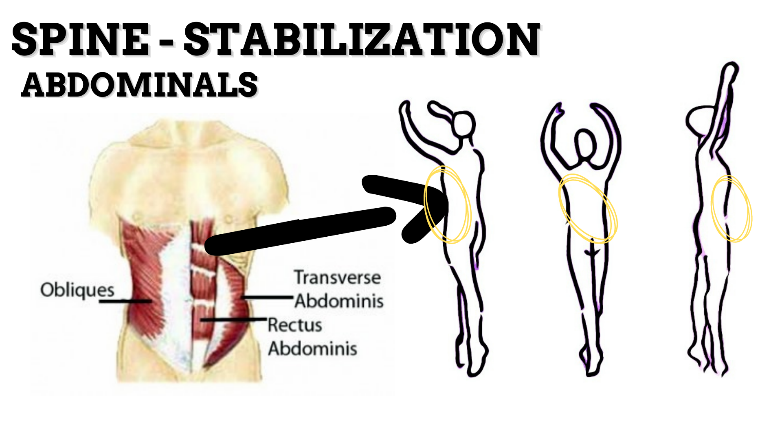
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: R SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
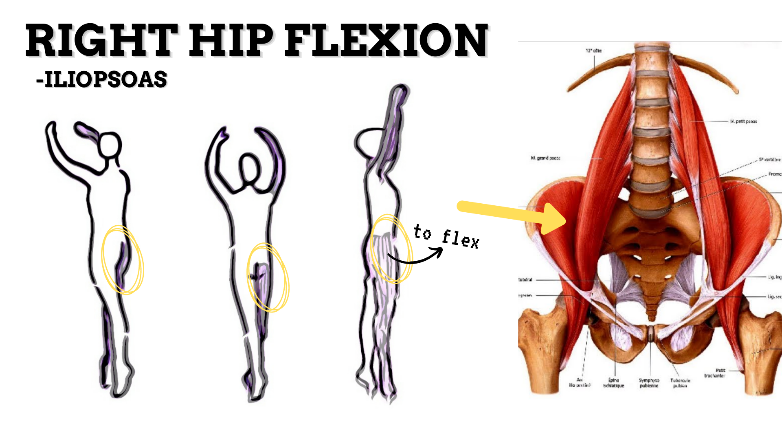
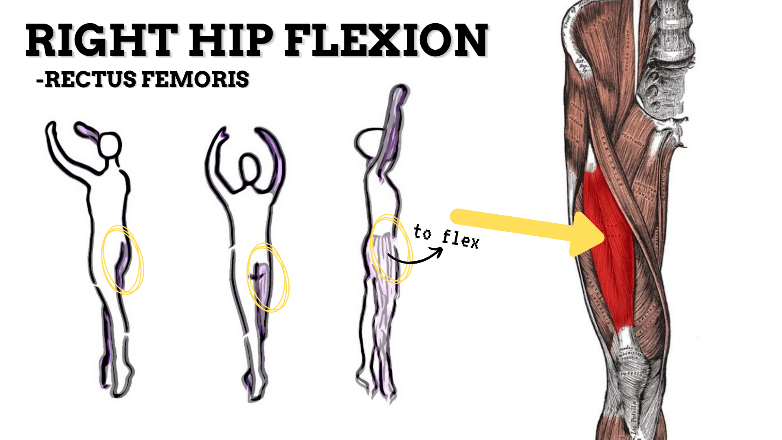
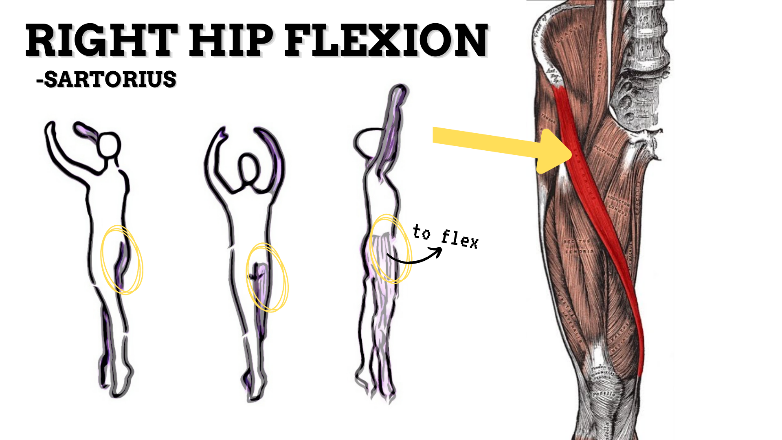
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ER, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
To achieve and maintain external rotation of the hip: Strengthen the deep lateral rotators or stretch the hip internal rotators, capsules, and anterior ligaments.
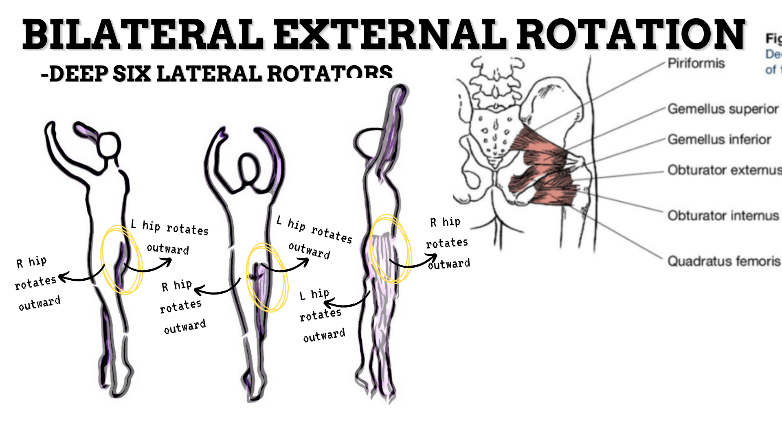
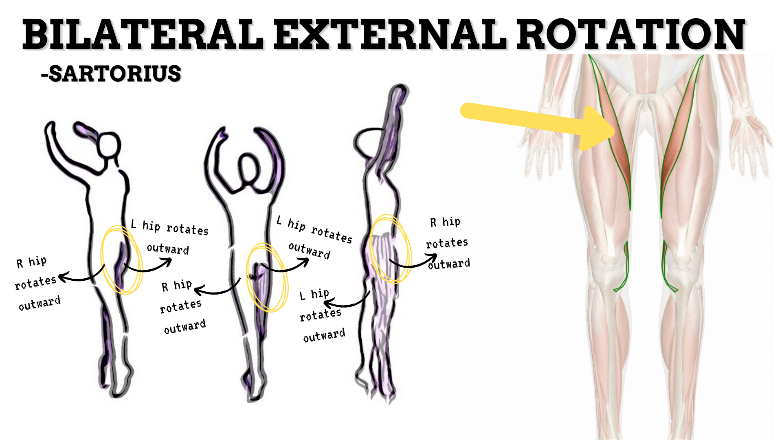
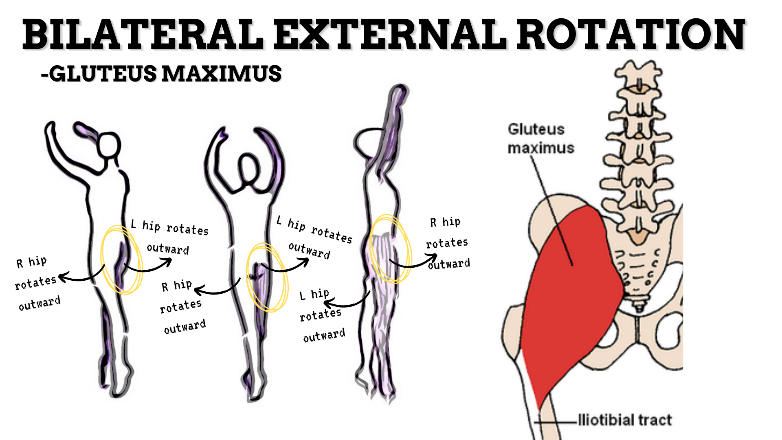
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: L SLIGHT EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
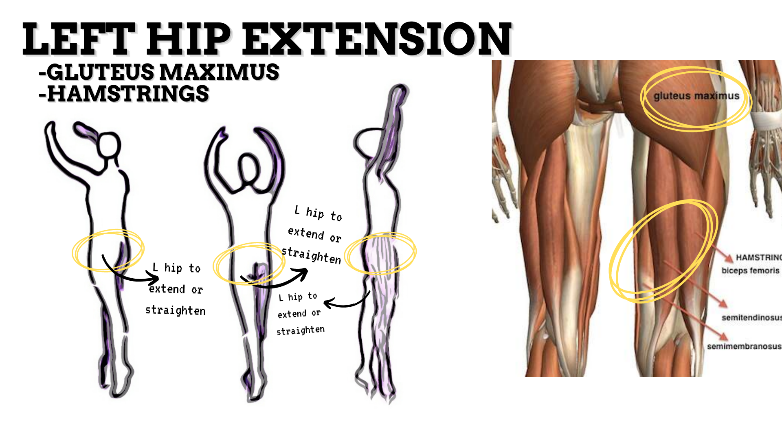
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
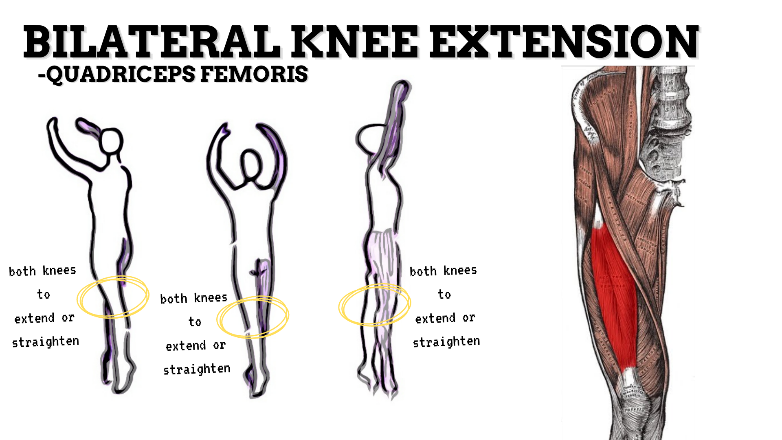
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
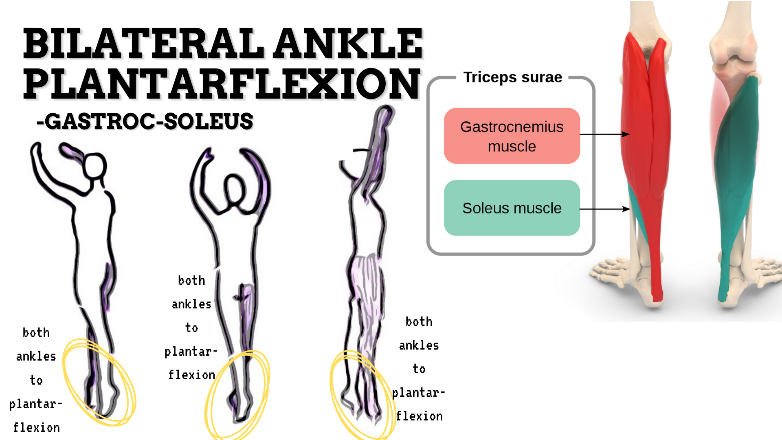
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL PF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
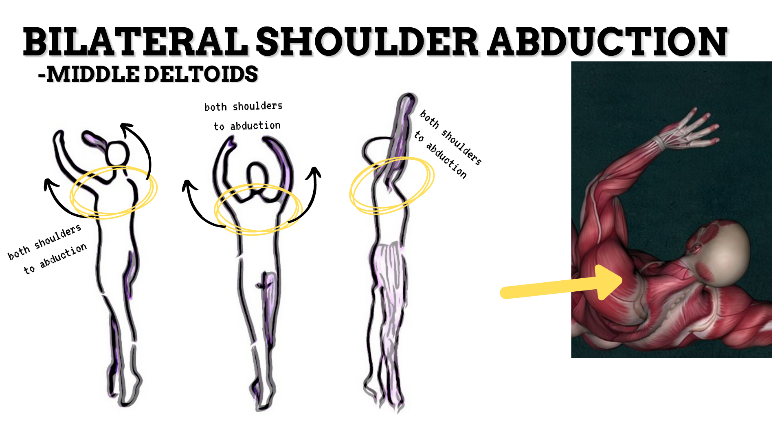
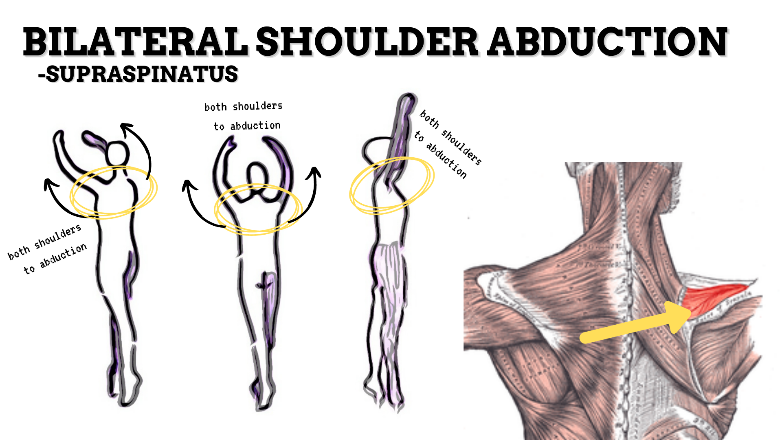
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ABDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
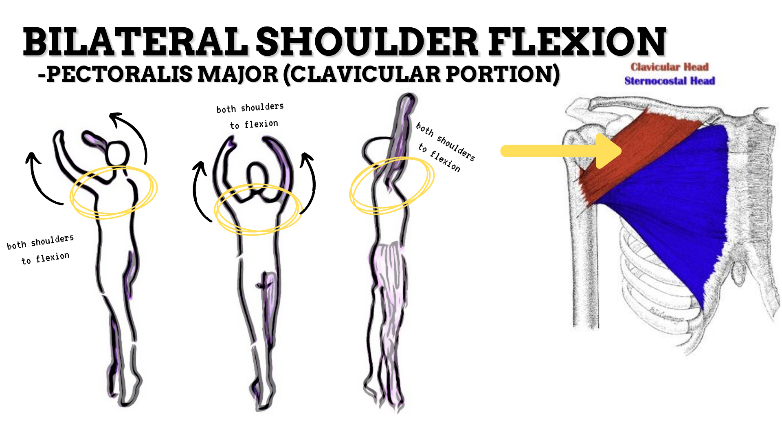
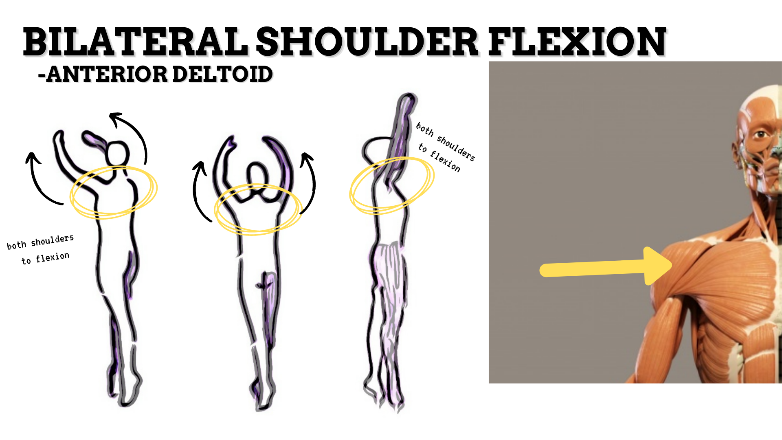
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
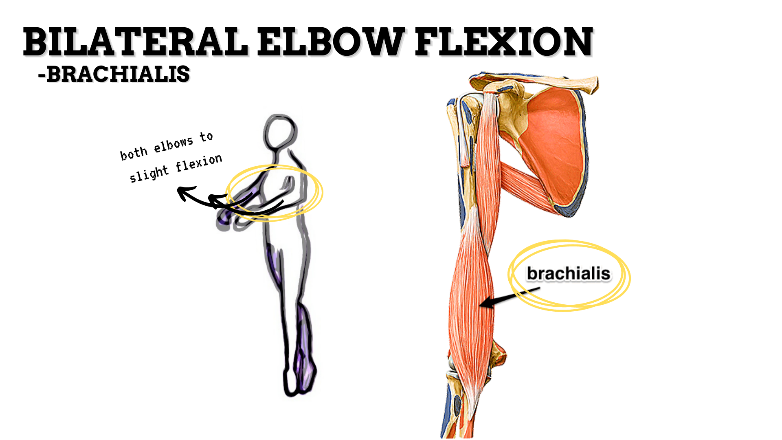
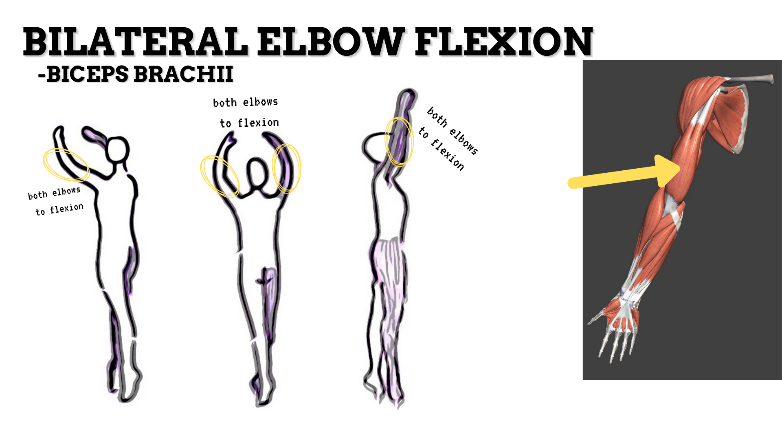
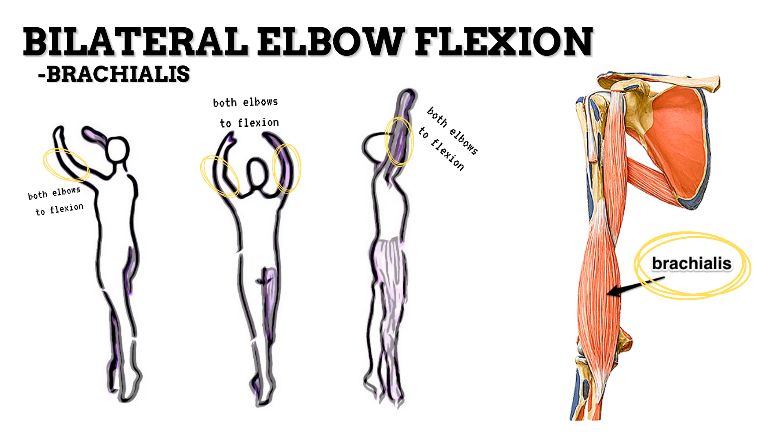
MAJOR JOINT: ELBOW
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
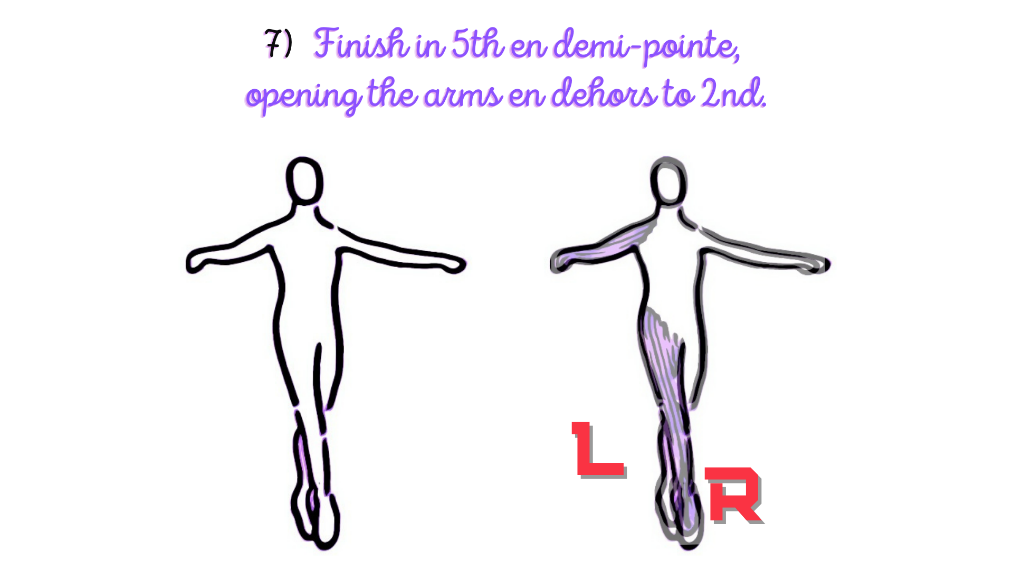
The seventh stance includes: to finish in 5th en demi-pointe, opening the arms en dehors to 2nd.
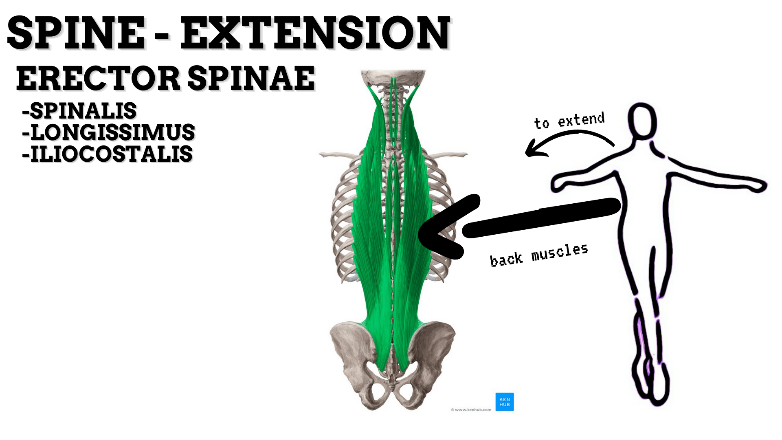
MAJOR JOINT: SPINE
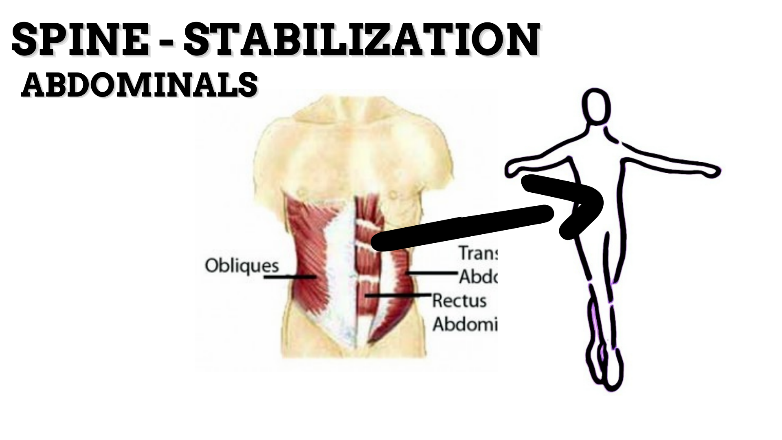
MOVEMENT: EXTENSION—concentric, Stabilized by eccentric contraction of ABDOMINALS
PRIME MOVER: RECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
PRIME MOVER: RECTOR SPINAE (Spinalis, Longissimus, and Iliocostalis)
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
MOVEMENT: R SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
PRIME MOVER: ILIOPSOAS, RECTUS FEMORIS, SARTORIUS
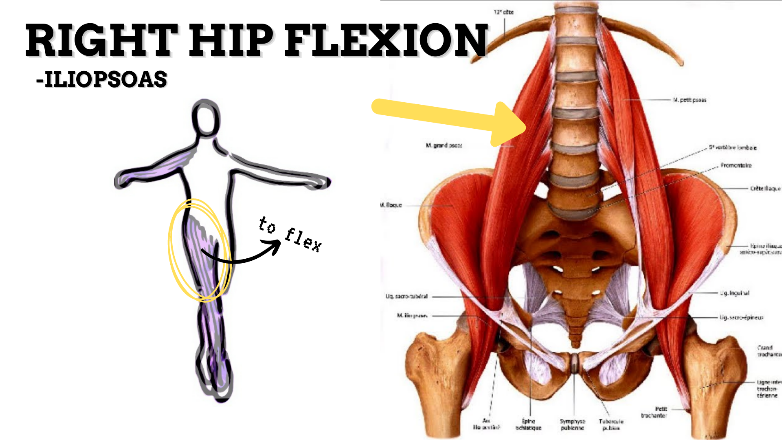
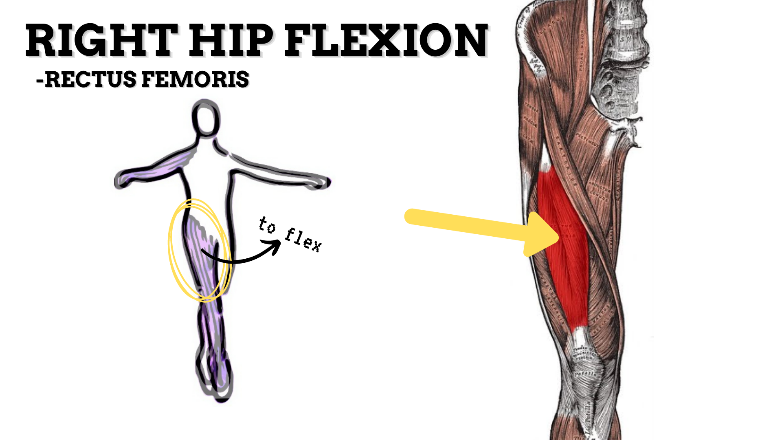
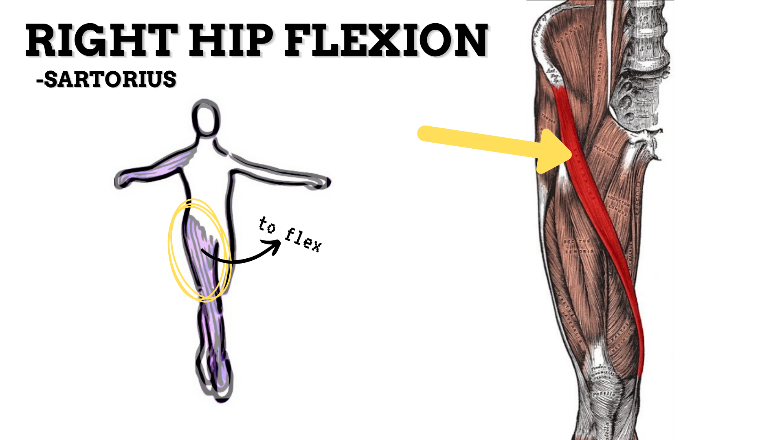
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
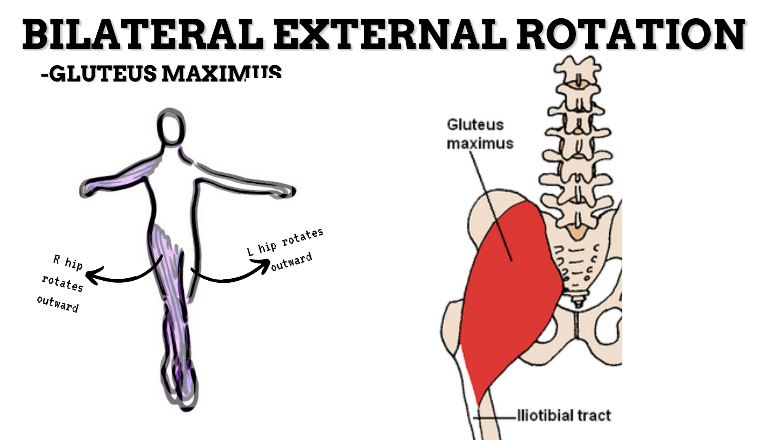
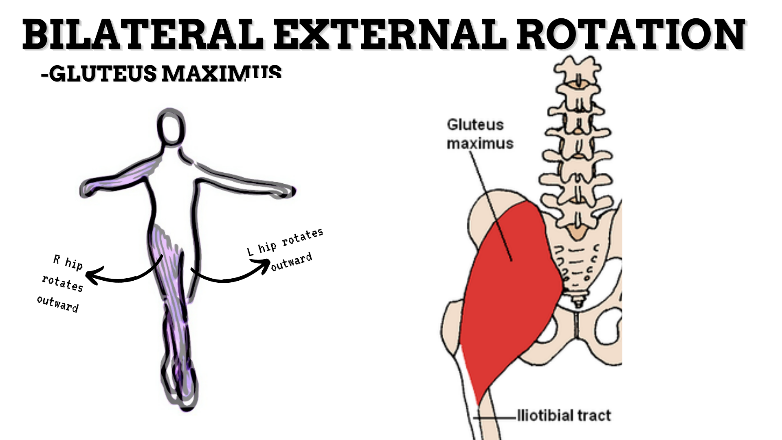
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ER, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
PRIME MOVER: GLUTEUS MAXIMUS, DEEP LATERAL ROTATORS, SARTORIUS
(ERs the hip especially with hip flexion)
To achieve and maintain external rotation of the hip: Strengthen the deep lateral rotators or stretch the hip internal rotators, capsules, and anterior ligaments.
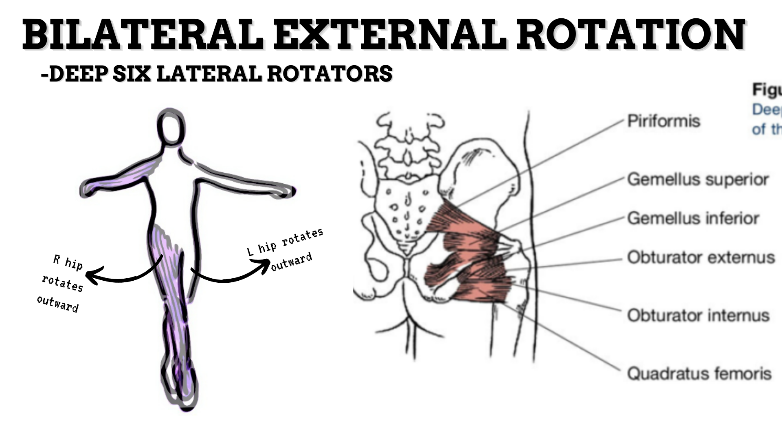
MAJOR JOINT: HIP
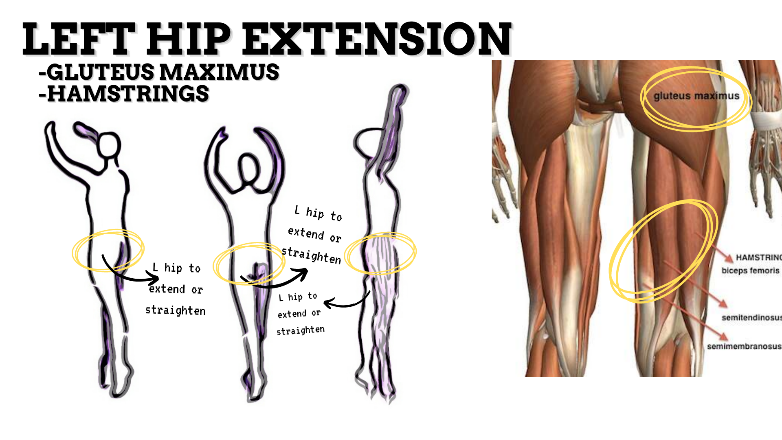
MOVEMENT: L SLIGHT EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
PRIME MOVER: HAMSTRINGS, GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
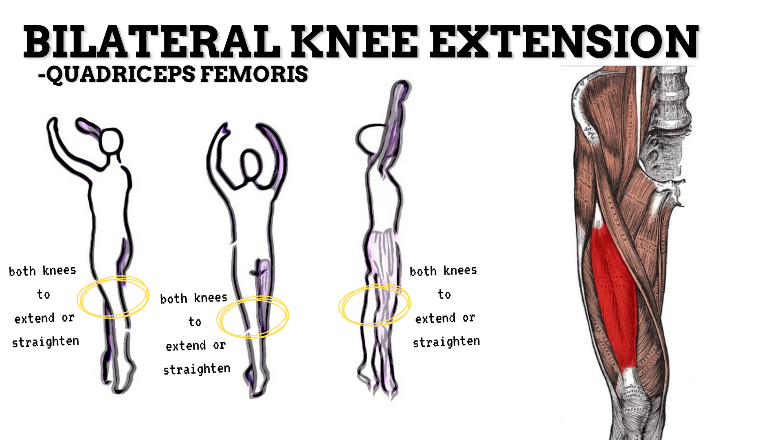
MAJOR JOINT: KNEE
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL EXTENSION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
PRIME MOVER: QUADRICEPS FEMORIS
To prevent excessive extension of the knee (knee hyperextension), strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and deep lateral rotators.
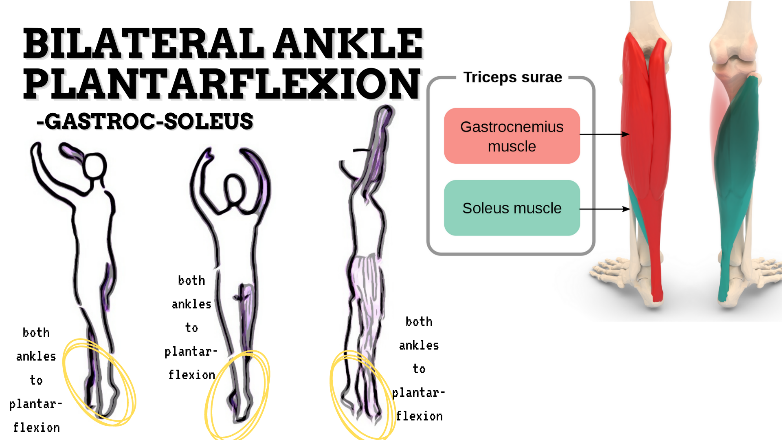
MAJOR JOINT: ANKLE-FOOT
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL PF, concentric
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
PRIME MOVER: GASTROCNEMIUS, SOLEUS
To prevent insufficient plantarflexion of foot, strengthen the ankle plantarflexors and intrinsic muscles (Tibialis posterior, FHL, FDL, FDB) that support the medial longitudinal arch of the foot; and stretch the dorsiflexors of the foot.
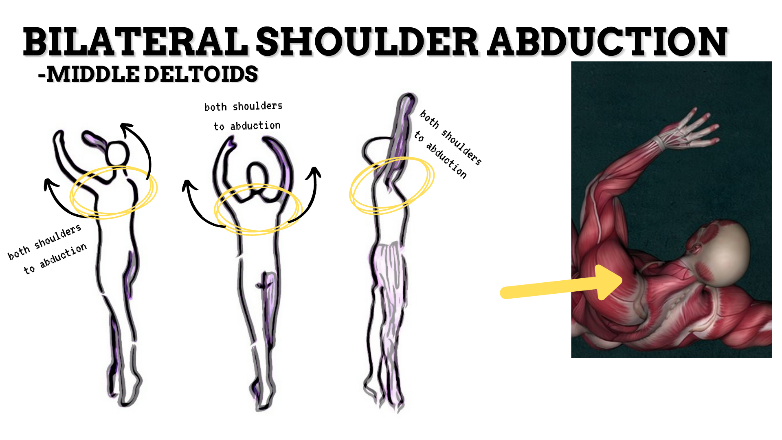
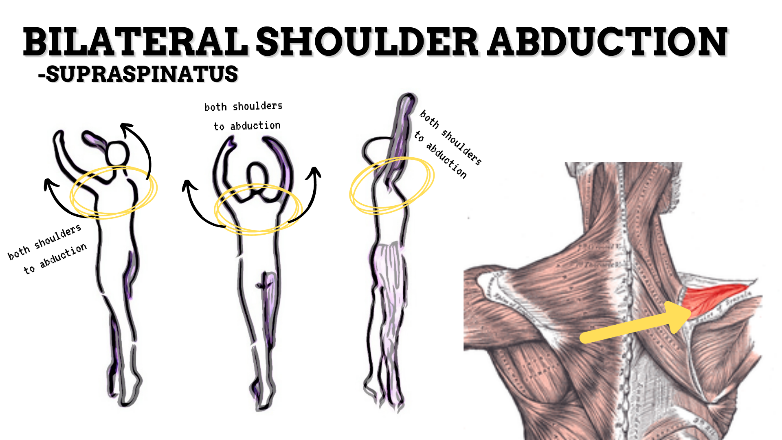
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL ABDUCTION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
PRIME MOVER: MIDDLE DELTOID, SUPRASPINATUS
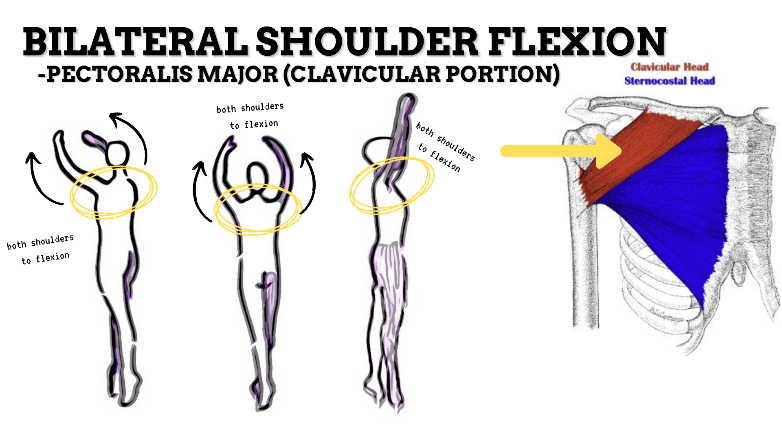
MAJOR JOINT: SHOULDER
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
PRIME MOVER: PECTORALIS MAJOR (CLAVICULAR), ANTERIOR DELTOID
To prevent rounded shoulders, stretch the shoulder internal rotators and horizontal adductors; and strengthen the scapular adductors, external rotators, and thoracic extensors.
MAJOR JOINT: ELBOW
MOVEMENT: BILATERAL SLIGHT FLEXION, concentric
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
PRIME MOVER: BICEPS BRACHII, BRACHIALIS
Start working on your Ballet Techniques today! Click on the picture below to learn about our Ballet & Dance Combo:
© ElasticSteel Corp., EasyFlexibility, Paul Zaichik, et. El., 2022. No part of the materials available through ElasticSteel.com, EasyFlexiiblity.com, site may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated or reduced to any electronic medium or machine-readable form, in whole or in part, without prior written consent of Paul Zaichik EasyFlexibility.com, Elasticsteel.com.. Any other reproduction in any form without the permission of Paul Zaichik EasyFlexibility.com, Elasticsteel.com is prohibited. All materials contained on this site are protected by United States copyright law and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior written permission of Paul Zaichik, EasyFlexibility.com, Elasticsteel.com.
Share this post
1 comment






great post Paul, but I don’t see a soutenu program in the store???